Welcome to our post on the Class 12 Chemistry specific grid, curriculum, syllabus, and model question for the Nepal Examination Board (NEB) board exam in 2080.
The NEB has recently updated the syllabus and curriculum for the Class 12 Chemistry course.
The syllabus covers various topics including inorganic, applied, physical and organic chemistry.
The specific grid for the exam includes a total of 11 multiple choice questions worth 11 marks, 8 short answer questions worth 40 marks, and 3 long answer questions worth 24 marks.
Table of Contents
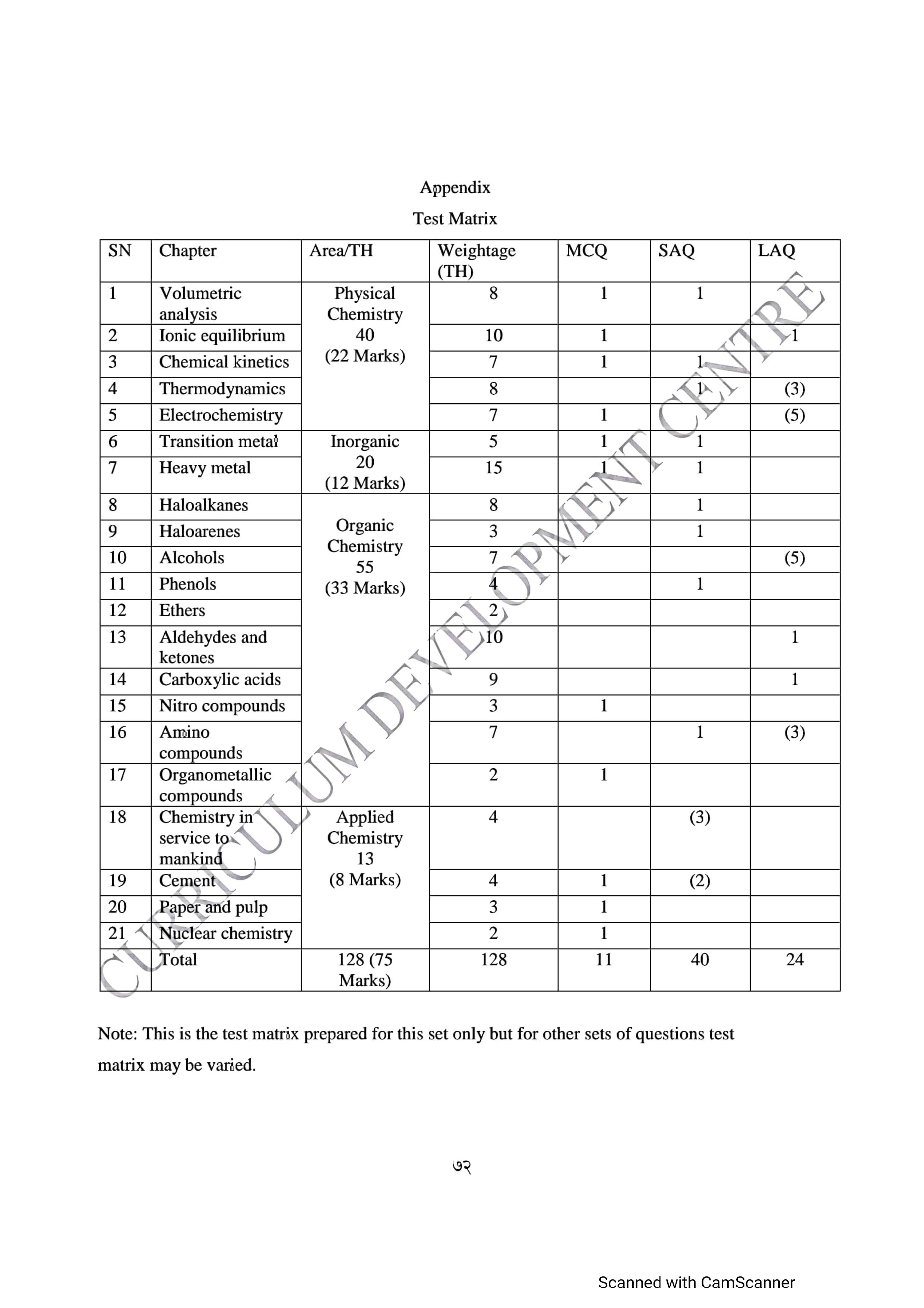
Specification Grid – Class 12 Chemistry
The Nepal Examination Board (NEB) has released the specification grid for Class 12 Chemistry, which outlines the format and content of the exam.
| Question Type | Number of Questions | Total Marks |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple Choice | 11 * 1 | 11 |
| Short Answer | 8 * 5 | 40 |
| Long Answer | 3 * 8 | 24 |
Additionally, an appendix has been provided which contains additional information and resources that can aid in Your exam preparation is given as:
Syllabus, Curriculum – Class 12 Chemistry
It covers a wide range of topics, including inorganic, applied, physical, and organic chemistry, to help students prepare for the upcoming NEB board exam in 2079.
General and Physical Chemistry
Unit 1. Volumetric Analysis (8 hrs)
1.1 Introduction to gravimetric analysis, volumetric analysis, and equivalent weight
1.2 Relationship between equivalent weight, atomic weight, and valency
1.3 Equivalent weight of compounds (acid, base, salt, oxidizing and reducing agents)
1.4 Concentration of solution and its units in terms of Percentage, g/L, molarity, molality, normality, and formality, ppm and ppb
1.5 Primary and secondary standard substances
1.6 Law of equivalence and normality equation
1.7 Titration and its types: Acid-base titration, redox titration ( related numerical problems)
Unit 2. Ionic Equilibrium (10 hrs)
Introduction to Acids and Bases
2.1. Limitation of Arrhenius’s concepts of acids and bases
2.2 Bronsted –Lowry definition of acids and bases
2.3 Relative strength of acids and bases
2.4 Conjugate acid-base pairs
2.5 Lewis’s definition of acids and bases
2.6 Ionization of weak electrolyte (Ostwald’s dilution law)
2.7 Ionic product of water(Kw)
2.8 Dissociation constant of acid and base, (Ka& Kb)
2.9 Concept of pKa and pKb
2.10 pH value: pH of strong and weak acids, pH of strong and weak bases
2.11 Solubility and solubility product principle
2.12 Common Ion effect
2.13 Application of solubility product principle and common ion effect in precipitation reactions
2.14 Buffer solution and its application
2.15 Indicators and selection of indicators in acid-base titration
2.16 Types of salts: Acidic salts, basic salts, simple salts, complex salts (introduction and examples)
2.17 Hydrolysis of salts
2.17.1 Salts of strong acid and strong base
2.17.2 Salts of a weak acid and strong base
2.17.3 Salts of a weak base and strong acid (solving related numerical problems)
Unit 3. Chemical kinetics (7 hrs)
3.1 Introduction
3.2 Rate of reactions: Average and instantaneous rate of reactions
3.3 Rate law and its expressions
3.4 Rate constant and it’s unit and significance
3.5 Order and molecularity
3.6 Integrated rate equation for zero and first-order reaction
3.7 Half-life of zero and first-order reactions
3.8 Collision theory, the concept of activation energy and activated complex
3.9 Factors affecting the rate of reactions: Effect of concentration, temperature (Arrhenius Equation), and effect of catalyst (energy profile diagram)
3.10 Catalysis and types of catalysis: homogeneous, heterogeneous, and enzyme catalysis (solving related numerical problems based on rate, rate constant, and order of zero and first-order reactions)
Unit 4. Thermodynamics (8 hrs)
4.1 Introduction
4.2 Energy in chemical reactions
4.3 Internal energy
4.4 First law of thermodynamics
4.5 Enthalpy and enthalpy changes: Endothermic and exothermic processes)
4.6 Enthalpy of reaction, enthalpy of solution, enthalpy of formation, enthalpy of combustion
4.7 Laws of thermochemistry (Laplace’s Law and Hess’s law)
4.8 Entropy and spontaneity
4.9 Second law of thermodynamics
4.10 Gibbs’ free energy and prediction of spontaneity
4.11 Relationship between ∆G and equilibrium constant (Solving related numerical problems)
Unit 5. Electrochemistry (7 hrs)
5.1 Electrode potential and standard electrode potential
5.2 Types of electrodes: Standard hydrogen electrodes and calomel electrodes
5.3 Electrochemical series and its applications
5.4 Voltaic cell: Zn-Cu cell, Ag- Cu cell
5.5 Cell potential and standard cell potential
5.6 Relationship between cell potential and free energy
5.7 Commercial batteries and fuel cells (hydrogen/oxygen)
Inorganic chemistry
Unit 6. Transition metals (5 hrs)
6.1 Introduction
6.1.1 Characteristics of transition metals
6.1.2 Oxidation states of transition metals
6.1.3 Complex ions and metal complexes
6.1.4 Shapes of complex ions
6.1.5 d-orbitals in complex ions (simple explanation by crystal field theory) for octahedral complex
6.1.6 Reasons for the color of transition metal compounds
6.1.7 Catalytic properties of transition metals
Unit 7. Studies of heavy metals (15 hrs)
7.1 Copper
7.1.1 Occurrence and extraction of copper from copper pyrite
7.1.2 Properties (with air, acids, aqueous ammonia, and metal ions) and uses of copper
7.1.3 Chemistry (preparation, properties, and uses) of blue vitriol
7.1.4 Other compounds of copper (red oxide and black oxide of copper) formula and uses only
7.2 Zinc
7.2.1 Occurrence and extraction of zinc from zinc blende
7.2.2 Properties (with air, acid, alkali, displacement reaction) and uses of zinc
7.2.3 Chemistry (preparation, properties, and uses) of white vitriol
7.3 Mercury
7.3.1 Occurrence and extraction of mercury from cinnabar
7.3.2 Properties of mercury
7.3.3 Chemistry (preparation, properties, and uses) of calomel and corrosive sublimate
7.4 Iron
7.4.1 Occurrence and extraction of iron
7.4.2 Properties and uses of iron
7.4.3 Manufacture of steel by Basic Oxygen Method and Open Hearth Process
7.4.4 Corrosion of iron and its prevention
7.5 silver
7.5.1 Occurrence and extraction of silver by cyanide process
7.5.2 Preparation and uses of silver chloride and silver nitrate
Organic chemistry
Unit 8. Haloalkanes (8 hrs)
8.1 Introduction
8.2 Nomenclature, isomerism, and classification of monohaloalkanes
8.3 Preparation of mono-haloalkanes from alkanes, alkenes, and alcohols
8.4 Physical properties of monohaloalkanes
8.5 Chemical properties, substitution reactions SN1 and SN2 reactions (basic concept only)
8.6 Formation of alcohol, nitrile, amine, ether, thioether, carbylamines, nitrite, and nitro alkane using haloalkanes
8.7 Elimination reaction (dehydrohalogenation- Saytzeff’s rule), Reduction reactions, Wurtz reaction
8.8 Preparation of trichloromethane from ethanol and propanone
8.9 Chemical properties of trichloromethane: oxidation, reduction, action on silver powder, conc. nitric acid, propanone, and aqueous alkali
Unit 9. Haloarenes (3 hrs)
9.1 Introduction
9.2 Nomenclature and isomerism of haloarenes
9.3 Preparation of chlorobenzene from benzene and benzene diazonium chloride
9.4 Physical properties
9.5 Chemical properties
9.5.1 Low reactivity of haloarenes as compared to haloalkanes in terms of nucleophilic substitution reaction
9.5.2 Reduction of chlorobenzene
9.5.3 Electrophilic substitution reactions
9.5.4 Action with Na (Fittig and Wurtz- Fittig reaction)
9.5.5 Action with chloral
9.6 Uses of haloarenes
Unit 10. Alcohols (7 hrs)
10.1 Introduction
10.2 Nomenclature, isomerism, and classification of monohydric alcohol
10.3 Distinction of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols by Victor Meyer’s Method
10.4 Preparation of monohydric alcohols from Haloalkane, primary amines, and esters
10.5 Industrial preparation alcohol from oxo process, hydroboration-oxidation of ethene & fermentation of sugar
10.6 Definition of common terms: Absolute alcohol, power alcohol, denatured alcohol (methylated spirit), rectified spirit; alcoholic beverage
10.7 Physical properties of monohydric alcohols
10.8 Chemical properties of monohydric alcohols
10.8.1 Reaction with HX, PX3, PCl5, SOCl2
10.8.2 Action with reactive metals like Na, K, Li
10.8.3 Dehydration of alcohols
10.8.4 Oxidation of primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohol with mild oxidizing agents like acidified KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7
10.8.5 Catalyic dehydrogenation of 1° and 2°alcohol and dehydration of 3°alcohol
10.8.6 Esterification reaction
10.8.7 Test of ethanol
Unit 11. Phenols (4 hrs)
11.1 Introduction and nomenclature
11.2 Preparation of phenol from i. chlorobenzene ii. Diazonium salt and iii. benzene sulphonic acid
11.3 Physical properties of phenol
11.4 Chemical properties
11.4.1 Acidic nature of phenol (comparison with alcohol and water)
11.4.2 Action with NH3, Zn, Na, benzene diazonium chloride and phthalic anhydride
11.4.3 Acylation reaction, Kolbe’s reaction, Reimer-Tiemann’s reaction
11.4.4 Electrophilic substitution: nitration, sulphonation, bromination, and Friedel-Craft’s alkylation
11.5 Test of phenol: (FeCl3 test, aq. Bromine test & Libermann test)
11.6 Uses of phenol
Unit 12. Ethers (2 hrs)
12.1 Introduction
12.2 Nomenclature, classification, and isomerism of ethers
12.3 Preparation of aliphatic and aromatic ethers from Williamson’s synthesis
12.4 Physical properties of ether
12.5 Chemical properties of ethoxyethane: action with HI, Conc. HCl, Conc. H2SO4, air and Cl2
12.6 Uses of ethers
Unit 13. Aldehydes and ketones (10 hrs)
13.1 Aliphatic aldehydes and ketones
13.1.1 Introduction, nomenclature, and isomerism
13.1.2 Preparation of aldehydes and ketones from Dehydrogenation and oxidation of alcohol, Ozonolysis of alkenes, Acid chloride, Gem dihaloalkane, Catalytic hydration of alkynes
13.1.3 Physical properties of aldehydes and ketones
13.1.4 Chemical properties
13.1.4.1 Structure and nature of carbonyl group
13.1.4.2 Distinction between aldehyde and ketones by using 2,4- DNP reagent, Tollen’s reagent, Fehling’s solution
13.1.4.3 Addition reaction: addition of H2, HCN and NaHSO3
13.1.4.4 Action of aldehyde and ketone with ammonia derivatives; NH2OH, NH2-NH2, phenyl hydrazine, semicarbazide,
13.1.4.5 Aldol condensation
13.1.4.6 Cannizzaro’s reaction
13.1.4.7 Clemmensen’s reduction
13.1.4.8 Wolf-Kishner reduction
13.1.4.9 Action with PCl5 and action with LiAlH4
13.1.4.10 Action of methanal with ammonia and phenol
13.1.5 Formalin and its uses
13.2 Aromatic aldehydes and Ketones
13.2.1 Preparation of benzaldehyde from toluene and acetophenone from benzene
13.2.2 Properties of benzaldehyde
13.2.2.1 Perkin condensation
13.2.2.2 Benzoin condensation
13.2.2.3 Cannizzaro’s reaction
13.2.2.4 Electrophilic substitution reaction
Unit 14. Carboxylic acid and its derivatives (9 hrs)
14.1 Aliphatic and aromatic carboxylic acids
14.1.1 Introduction, nomenclature, and isomerism
14.1.2 Preparation of monocarboxylic acids from aldehydes, nitriles, dicarboxylic acid, sodium alkoxide, and trihaloalkanes
14.1.3 Preparation of benzoic acid from alkyl benzene
14.1.4 Physical properties of monocarboxylic acids
14.1.5 Chemical properties: Action with alkalies, metal oxides, metal carbonates, metal bicarbonates, PCl3, LiAlH4, and dehydration of carboxylic acid
14.1.6 Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction
14.1.7 Electrophilic substitution reaction of benzoic acid – bromination, nitration, and sulphonation)
14.1.8 Effect of constituents on the acidic strength of carboxylic acid
14.1.9 Abnormal behavior of methanoic acid
14.2 Derivatives of Carboxylic acids (acid halides, amides, esters, and anhydrides)
14.2.1 Preparation of acid derivatives from carboxylic acid
14.2.2 Comparative physical properties of acid derivatives
14.2.3 Comparative chemical properties of acid derivatives (hydrolysis, ammonolysis, amines (RNH2), alcoholysis, and reduction only)
14.2.4 Claisen condensation
14.2.5 Hofmann bromamide reaction
14.2.6 Amphoteric nature of amide
14.2.7 Relative reactivity of acid derivatives
Unit 15. Nitro compounds (3 hrs)
15.1 Nitroalkanes
15.1.1 Introduction, nomenclature, and isomerism
15.1.2 Preparation from haloalkane and alkane
15.1.3 Physical properties
15.1.4 Chemical properties: Reduction
15.2 Nitrobenzene
15.2.1 Preparation from benzene
15.2.2 Physical properties
15.2.3 Chemical properties
15.2.4 Reduction in different media
15.2.5 Electrophilic substitution reactions (nitration, sulphonation & bromination)
15.2.6 Uses of nitro-compounds
Unit 16. Amines (7 hrs)
16.1 Aliphatic amines
16.1.1 Introduction, nomenclature, classification, and isomerism
16.1.2 Separation of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines by Hoffmann’s method
16.1.3 Preparation of primary amines from haloalkane, nitriles, nitroalkanes, and amides
16.1.4 Physical properties
16.1.5 Chemical properties: basicity of amines, comparative study of basic nature of 1°, 2°, and 3° amines
16.1.6 Reaction of primary amines with chloroform, conc. HCl, R-X, RCOX, and nitrous acid (NaNO2 / HCl)
16.1.7 Test of 1, 2, and 3 amines (nitrous acid test)
16.2 Aromatic amine (Aniline)
16.2.1 Preparation of aniline from nitrobenzene, phenol
16.2.2 Physical properties
16.2.3 Chemical properties: basicity of aniline, comparison of basic nature of aniline with aliphatic amines and ammonia, alkylation, acylation, diazotization, carbylamine and coupling reaction, electrophilic substitution: Nitration sulphonation and bromination
16.2.4 Uses of aniline
Unit 17. Organometallic compounds (2 hrs)
17.1 Introduction, general formula, and examples of organolithium, organocopper, and organocadmium compounds
17.2 Nature of Metal-Carbon bond
17.3 Grignard reagent
17.3.1 Preparation (using haloalkane and haloarene)
17.3.2 Reaction of the Grignard reagent with water, aldehydes, and ketones ( preparation of primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols), carbon dioxide, HCN, RCN, ester, and acid chloride
Applied Chemistry
Unit 18. Chemistry in the service of mankind (4 hrs)
18.1 Polymers
18.1.1 Addition and condensation polymers
18.1.2 Elastomers and fibers
18.1.3 Natural and synthetic polymers
18.1.4 Some synthetic polymers (polyethylene, PVC, Teflon, polystyrene, nylon, and Bakelite)
18.2 Dyes
18.2.1 Introduction
18.2.2 Types of dyes based on structure and method of application
18.3 Drugs
18.3.1 Characteristics of drugs
18.3.2 Natural and synthetic drugs
18.3.3 Classification of some common drugs
18.3.4 Habit-forming drugs and drug addiction
18.4 Pesticides
18.4.1 Introduction to insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides
Unit 19. Cement (4 hrs)
19.1 Introduction
19.2 Raw materials for cement production
19.3 Main steps in cement production (crushing and grinding, strong heating, and final grinding)
19.4 Types of cement- OPC and PPC
19.5 Portland cement process with flow-sheet diagram
19.6 Cement Industry in Nepal
Unit 20. Paper and pulp (3 hrs)
20.1 Introduction
20.2 Raw materials
20.3 Sources of raw materials
20.4 Stages in the production of paper
20.5 Flow-sheet diagram for paper production
20.6 Quality of paper
Unit 21. Nuclear chemistry and application of radioactivity (2 hrs)
21.1 Natural and artificial radioactivity
21.2 Units of radioactivity
21.3 Nuclear reactions
21.4 Nuclear fission and fusion reactions
21.5 Nuclear power and nuclear weapons
21.6 Industrial uses of radioactivity
21.7 Medical uses of radioactivity
21.8 Radiocarbon dating
21.9 Harmful effects of nuclear radiation
Related Posts
Download Syllabus Class 11 and Class 12 Chemistry
Model Question – Class 12 Chemistry
The model question for Class 12 Chemistry for the 2079 Nepal Examination Board (NEB) board exam is an essential tool for students preparing for the exam. This can help students to become familiar with the format and structure of the exam.
This can include inorganic chemistry, applied chemistry, physical chemistry, and organic chemistry, as well as topics such as chemical reactions, thermochemistry, kinetics, and equilibrium including multiple choice questions, short answer questions, and long answer questions.
Class 12 Chemistry Model Question for NEB Exam 2079 is given as:
Download Model Question Class 12 Chemistry
Read more:








![NEB Class 12 Exam Routine 2081/2082 [2025]](https://iswori.com.np/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/neb-class-12-routine.png)
