Welcome to our post on the Class 12 physics specific grid, curriculum, syllabus, and model question for the Nepal Examination Board (NEB) board exam in 2080. In this post, we will provide students with all the necessary information they need to succeed in their Class 12 physics exams.
The NEB has recently updated the syllabus and curriculum for the Class 12 physics course, and we will outline all the key changes and updates in this post.
We will also provide a comprehensive overview of the Class 12 physics specific grid, which outlines the distribution of marks for different types of questions in the exam, as well as the weightage and format of different units and topics within the course. Finally, we will provide a selection of model questions that students can use to practice and prepare for the Class 12 physics exam.
Table of Contents
Chapters – Class 12 Physics
NEB Class 12 Physics Chapters for 2080 is given as:
| S.N. | Class 12 Physics Chapters |
|---|---|
| Content Area | Mechanics |
| Chapter 1 | Rotational dynamics |
| Chapter 2 | Periodic motion |
| Chapter 3 | Fluid statics |
| Content Area | Heat and Thermodynamics |
| Chapter 4 | First law of Thermodynamics |
| Chapter 5 | Second First law of Thermodynamics |
| Content Area | Wave and Optics |
| Chapter 6 | Wave motion |
| Chapter 7 | Mechanical waves |
| Chapter 8 | Wave in pipes and strings |
| Chapter 9 | Acoustic phenomena |
| Chapter 10 | Nature and propagation of light |
| Chapter 11 | Interference |
| Chapter 12 | Diffraction |
| Chapter 13 | Polarization |
| Content Area | Electricity and Magnetism |
| Chapter 14 | Electrical circuits |
| Chapter 15 | Thermoelectric effects |
| Chapter 16 | Magnetic field |
| Chapter 17 | Magnetic properties of materials |
| Chapter 18 | Electromagnetic Induction |
| Chapter 19 | Alternating currents |
| Content Area | Modern Physics |
| Chapter 20 | Electrons |
| Chapter 21 | Photons |
| Chapter 22 | Semiconductor devices |
| Chapter 23 | Quantization of energy |
| Chapter 24 | Radioactivity and nuclear reaction |
| Chapter 25 | Recent trends in Physics |
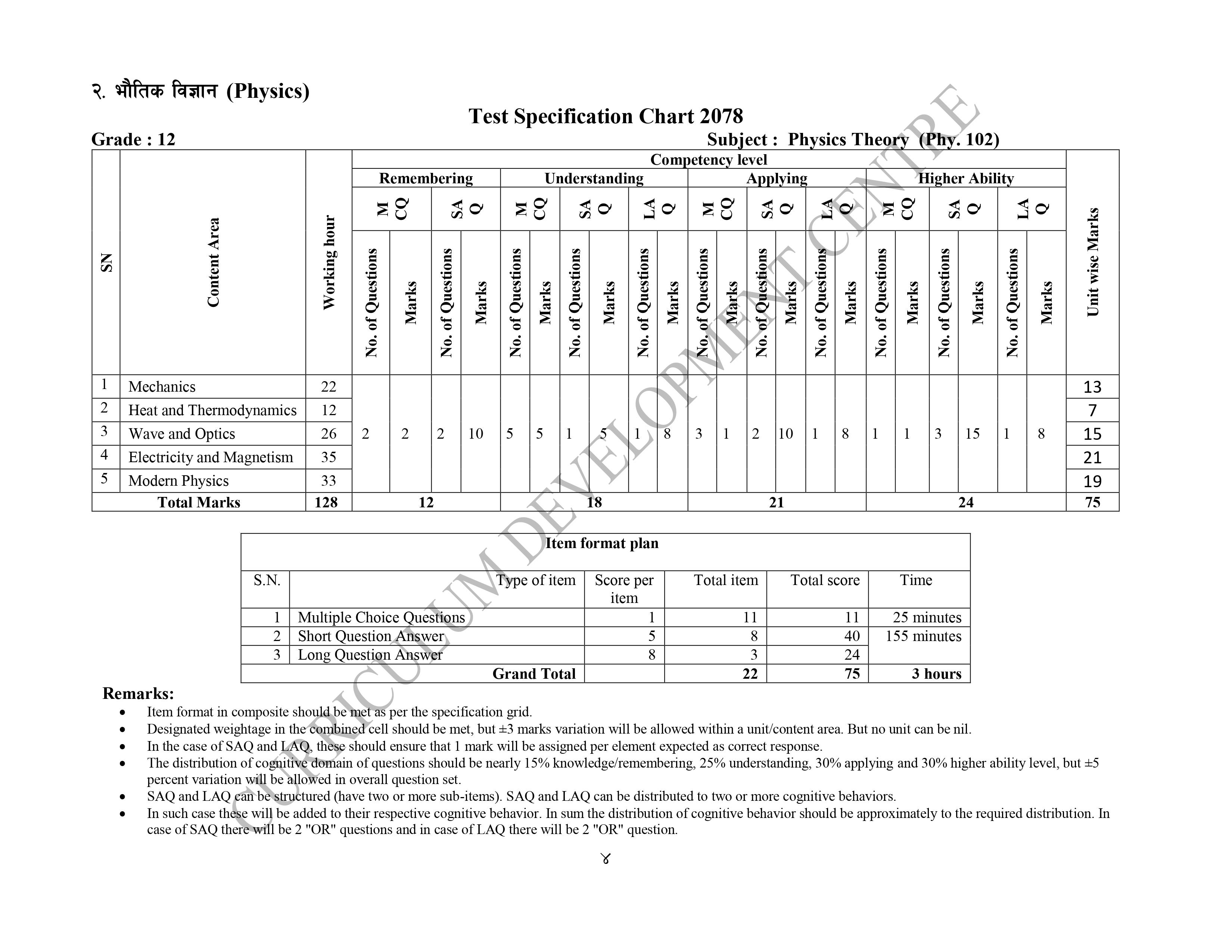
Specification Grid – Class 12 Physics
According to the information provided by CDC, the exam will include multiple choice questions (MCQs), short answer questions (SAQs), and long answer questions (LAQs).
The NEB Board exam of Physics will have
a total of 11 MCQs worth 11 marks,
8 SAQs worth 40 marks,
and 3 LAQs worth 24 marks.
The specification grid for the exam, issued by the Curriculum Development Center (CDC), provides further details on the format and content of the exam.
It is important for students to consult the specific grid provided by their instructor or school for the most accurate and up-to-date information about the Internal exam.
Physics Specific Grid for NEB Board Exam 2080 is Given as:
Syllabus, Curriculum – Class 12 Physics
The Nepal Examination Board (NEB) has recently updated the curriculum and syllabus for physics courses in grades 11 and 12. The curriculum is designed to provide students with a general understanding of the fundamental scientific laws and principles that govern scientific phenomena in the world.
It aims to develop the scientific knowledge, skills, and attitudes that are necessary for success at the secondary level, regardless of what students may choose to do after completing their studies. The curriculum is intended to be flexible and adaptable, catering to the diverse aspirations of students who may choose to pursue further studies in science, technical or vocational fields, or other areas.
The syllabus typically covers a range of topics, including mechanics, thermodynamics, waves and optics, electricity and magnetism, and modern physics.
In the mechanics section of the syllabus, students may study topics such as rotational dynamics, periodic motion, and fluid statics. The thermodynamics section may cover the first and second laws of thermodynamics, while the waves and optics section may cover topics such as wave motion, mechanical waves, wave behavior in pipes and strings, and the nature and propagation of light.
The electricity and magnetism section of the syllabus may include topics such as electrical circuits, thermoelectric effects, magnetic fields, and electromagnetic induction. The modern physics section may cover topics such as electrons, photons, semiconductor devices, and quantization of energy.
Class 12 Physics Syllabus and Curriculum for NEB Exam 2079/2080 is given as:
Unit | Content |
Mechanics | |
| 1. Rotational dynamics | 1.1 Equation of angular motion, Relation between linear and angular kinematics 1.2 Kinetic energy of rotation of rigid body 1.3 Moment of inertia; Radius of gyration 1.4 Moment of inertia of a uniform rod 1.5 Torque and angular acceleration for a rigid body 1.6 Work and power in rotational motion 1.7 Angular momentum, conservation of angular momentum. |
| 2. Periodic motion | 2.1 Equation of simple harmonic motion (SHM) 2.2 Energy in SHM 2.3 Application of SHM: vertical oscillation of mass suspended from coiled spring 2.4 Angular SHM, simple pendulum 2.5 Oscillatory motion: Damped oscillation, Forced oscillation and resonance. |
| 3. Fluid statics | 3.1 Fluid statics: Pressure in a fluid; Buoyancy 3.2 Surface tension: Theory of surface tension; Surface energy 3.3 Angle of contact, capillarity and its applications 3.4 Fluid Dynamics:Newton’s formula for viscosity in a liquid; Coefficient of viscosity 3.5 Poiseuille’s formula and its application 3.6 Stokes law and its applications 3.7 Equation of continuity and its applications 3.8 Bernoulli’s equation and its applications. |
Heat and Thermodynamics | |
| 4. First law of thermodynamics | 4.1 Thermodynamic systems 4.2 Work done during volume change 4.3 Heat and work; Internal energy and First law of thermodynamics 4.4 Thermodynamic processes: Adiabatic, isochoric, isothermal and isobaric 4.5 Heat capacities of an ideal gas at constant pressure and volume and relation between them 4.6 Isothermal and Adiabatic processes for an ideal gas. |
| 5. Second law of thermodynamics | 5.1 Thermodynamic systems and direction of thermodynamic processes 5.2 Second law of thermodynamics 5.3 Heat engines 5.4 Internal combustion engines: Otto cycle, Diesel cycle; Carnot cycle 5.5 Refrigerator 5.6 Entropy and disorder (introduction only) |
Wave and optics | |
| 6. Wave motion | 6.1 Progressive waves 6.2 Mathematical description of a wave 6.3 Stationary waves |
| 7. Mechanical waves | 7.1 Speed of wave motion; Velocity of sound in solid and liquid 7.2 Velocity of sound in gas 7.3 Laplace’s correction 7.4 Effect of temperature, pressure, humidity on velocity of sound. |
| 8. Wave in pipes and strings | 8.1 Stationary waves in closed and open pipes 8.2 Harmonics and overtones in closed and open organ pipes 8.3 End correction in pipes 8.4 Velocity of transverse waves along a stretched string 8.5 Vibration of string and overtones 8.6 Laws of vibration of fixed string. |
| 9. Acoustic phenomena | 9.1 Sound waves: Pressure amplitude 9.2 Characteristics of sound: Intensity; loudness, quality and pitch 9.3 Doppler’s effect. |
| 10. Nature and propagation of light | 10.1 Huygen’s principle 10.2 Reflection and Refraction according to wave theory |
| 11. Interference | 11.1 Phenomenon of Interferences: Coherent sources 11.2 Young’s double slit experiment. |
| 12. Diffraction | 12.1 Diffraction from a single slit 12.2 Diffraction pattern of image; Diffraction grating 12.3 Resolving power of optical instruments. |
| 13. Polarization | 13.1 Phenomenon of polarization 13.2 Brewster’s law; transverse nature of light 13.3 Polaroid. |
Electricity and Magnetism | |
| 14. Electrical circuits | 14.1 Kirchhoff’s law 14.2 Wheatstone bridge circuit; Meter bridge 14.3 Potentiometer: Comparison of e.m.f., measurement of internal resistances of a cell 14.4 Super conductors; Perfect conductors 14.5 Conversion of galvanometer into voltmeter and ammeter; Ohmmeter 14.6 Joule’s law |
| 15. Thermoelectric effects | 15.1 Seebeck effect; Thermocouples 15.2 Peltier effect: Variation of thermoelectric e.m.f. with temperature; Thermopile |
| 16. Magnetic field | 16.1 Magnetic field lines and magnetic flux; Oersted’s experiment 16.2 Force on moving charge; Force on a conductor 16.3 Force and Torque on rectangular coil, Moving coil galvanometer 16.4 Hall effect 16.5 Magnetic field of a moving charge 16.6 Biot and Savart law and its application to (i) a circular coil (ii) a long straight conductor (iii) a long solenoid 16.7 Ampere’s law and its applications to (i) a long straight conductor (ii) a straight solenoid (ii) a toroidal solenoid 16.8 Force between two parallel conductors carrying current- definition of ampere |
| 17. Magnetic properties of materials | 17.1 Magnetic field lines and magnetic flux 17.2 Flux density in magnetic material; Relative permeability; Susceptibility 17.3 Hysteresis 17.4 Dia,-para- and ferro-magnetic materials |
| 18. Electromagnetic Induction | 18.1 Faraday’s laws; Induced electric fields 18.2 Lenz’s law, Motional electromotive force 18.3 A.C. generators; Eddy currents 18.4 Self-inductance and mutual inductance 18.5 Energy stored in an inductor 18.6 Transformer. |
| 19. Alternating currents | 19.1 Peak and rms value of AC current and voltage 19.2 AC through a resistor, a capacitor and an inductor 19.3 Phasor diagram 19.4 Series circuits containing combination of resistance, capacitance and inductance 19.5 Series resonance, quality factor 19.6 Power in AC circuits: power factor |
Modern physics | |
| 20. Electrons | 20.1 Milikan’s oil drop experiment, 20.2 Motion of electron beam in electric and magnetic fields 20.3 Thomson’s experiment to determine specific charge of electrons |
| 21. Photons | 21.1 Quantum nature of radiation 21.2 Einstein’s photoelectric equation; Stopping potential 21.3 Measurement of Plank’s constant |
| 22. Semiconductor devices | 22.1 P-N Junction 22.2 Semiconductor diode: Characteristics in forward and reverse bias 22.3 Full wave rectification 22.5 Logic gates; NOT, OR, AND, NAND and NOR. |
| 23. Quantization of energy | 23.1 Bohr’s theory of hydrogen atom 23.2 Spectral series; Excitation and ionization potentials 23.3 Energy level; Emission and absorption spectra 23.4 De Broglie Theory; Duality 23.5 Uncertainly principle 23.6 X-rays: Nature and production; uses 23.7 X-rays diffraction, Bragg’s law. |
| 24. Radioactivity and nuclear reaction | 24.1 Alpha-particles; Beta-particles, Gamma rays 24.2 Laws of radioactive disintegration 24.3 Half-life, mean-life and decay constant 24.4 Geiger-Muller Tube 24.5 Carbon dating 24.6 Medical use of nuclear radiation and possible health hazard. |
| 25. Recent trends in physics | 25.1 Surface waves: Rayleigh and Love waves Internal waves: S and P-waves Wave patterns of Gorkha Earthquake 2015 25.2 Gravitational Wave Nanotechnology Higgs Boson |
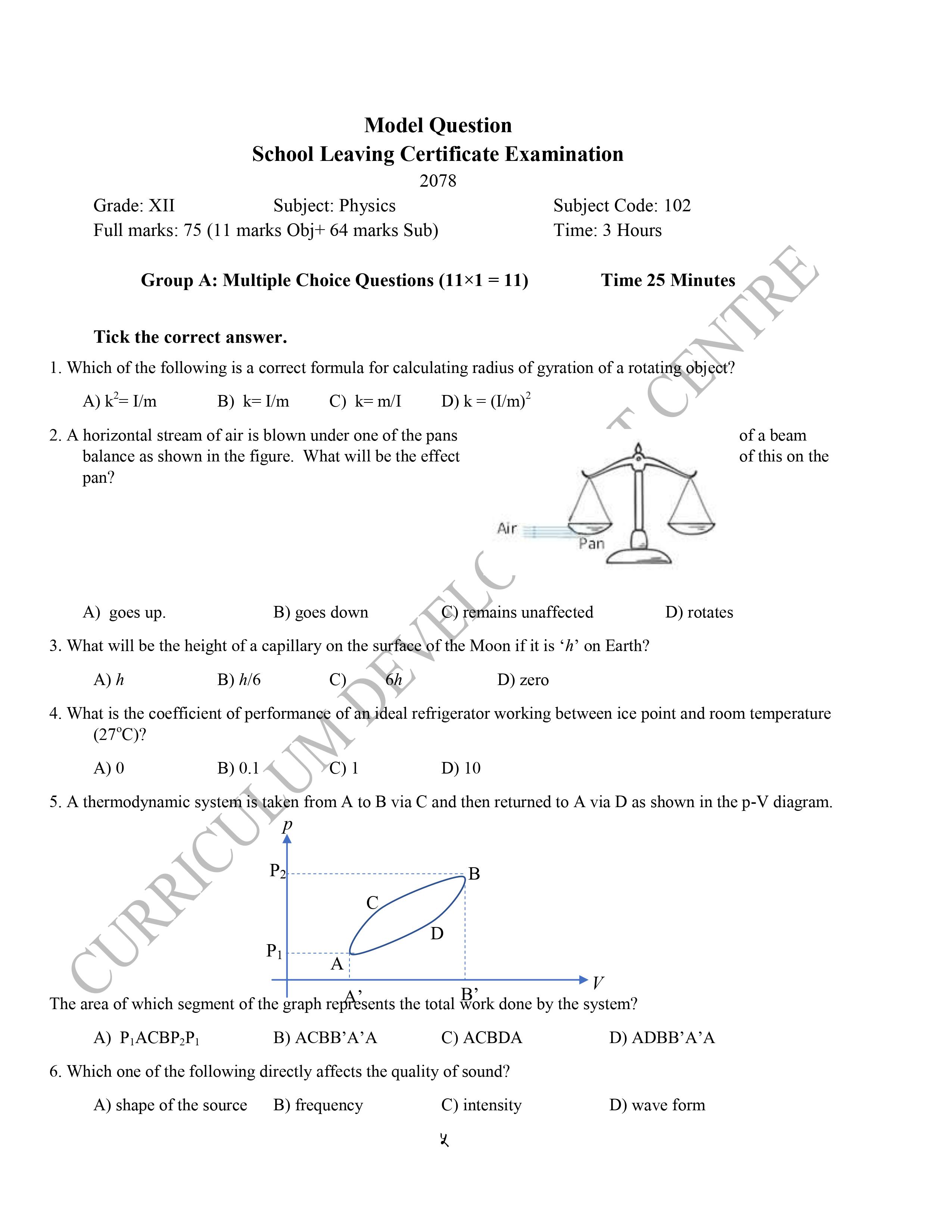
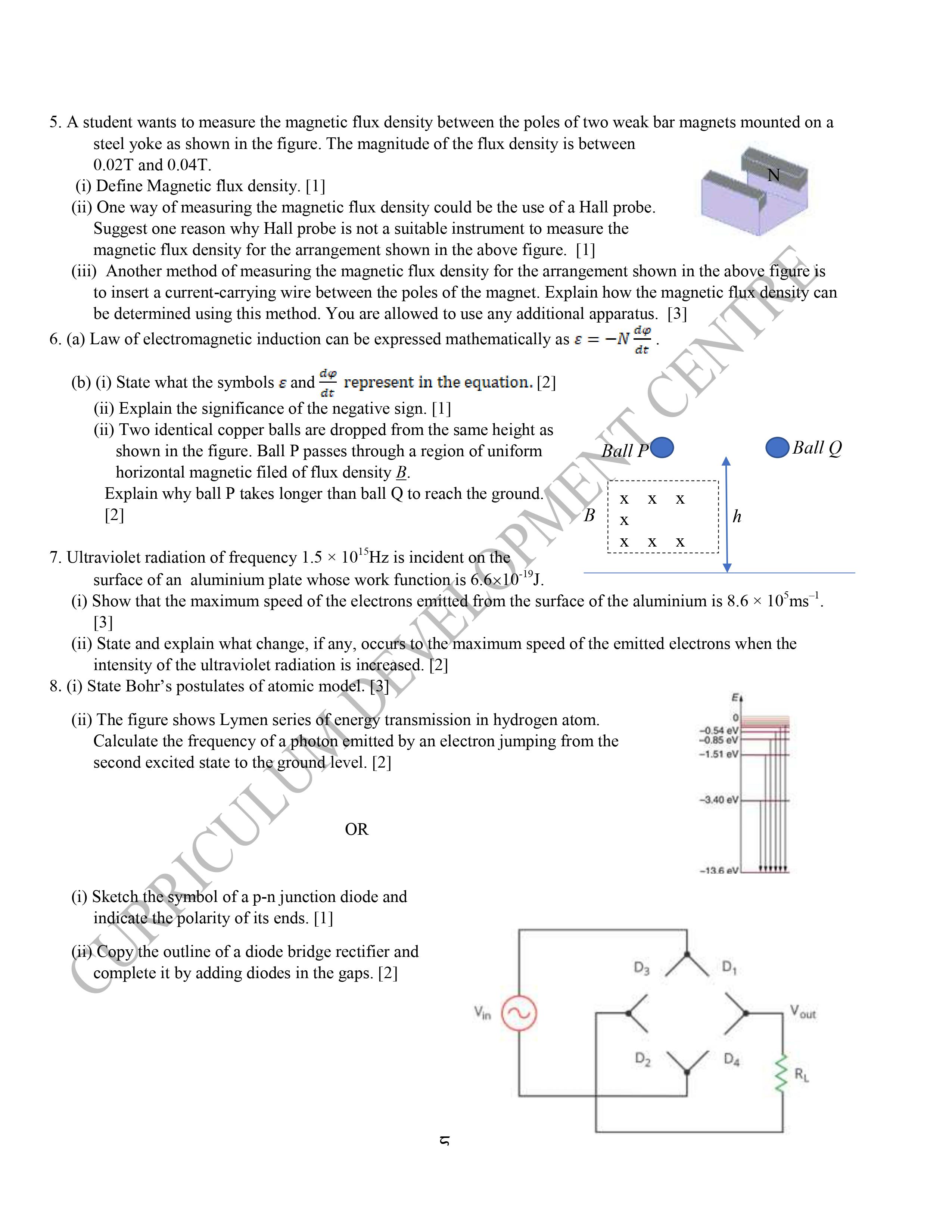
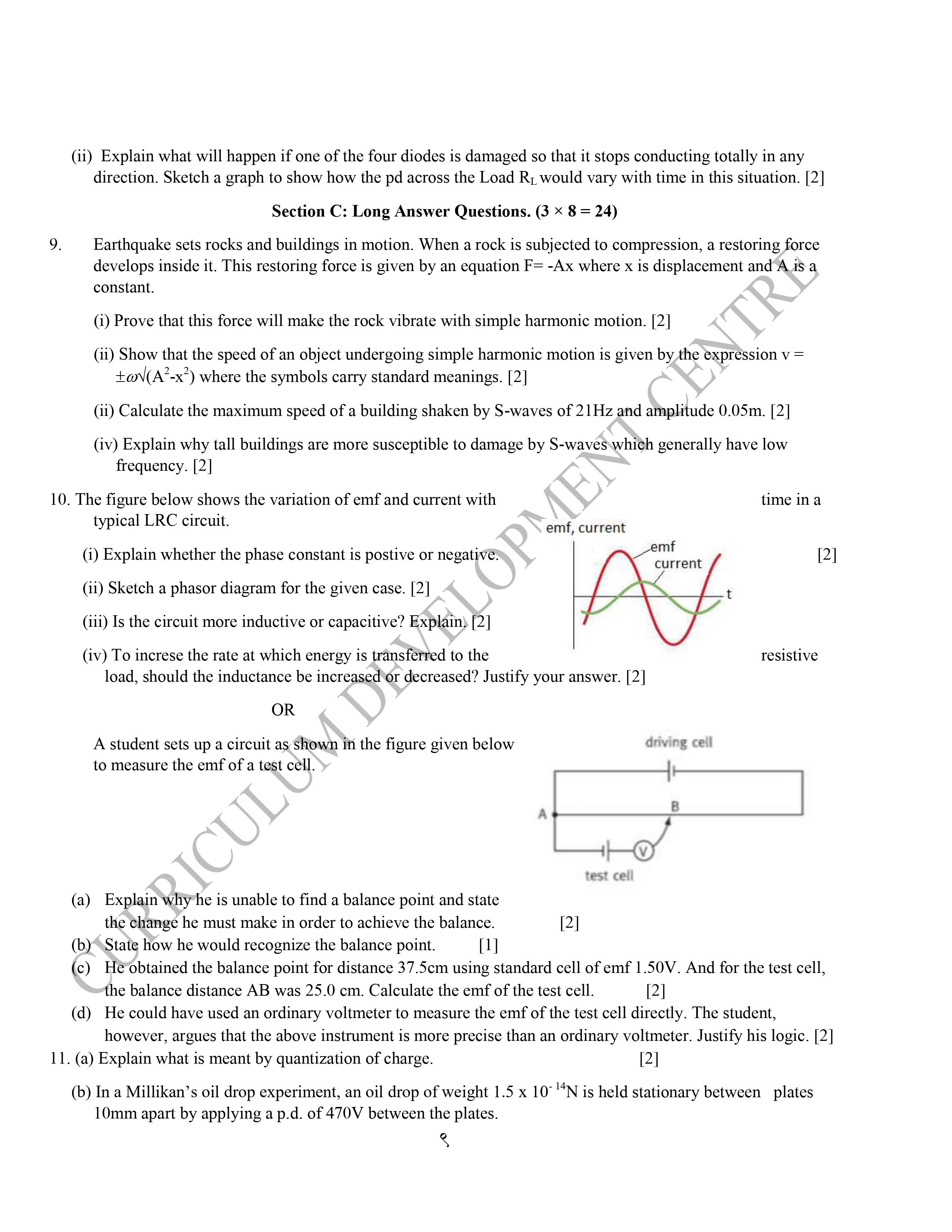
Model Question 2079 – Class 12 Physics
Class 12 physics model questions provided in this post are designed to help students prepare for the NEB board exam in 2079. These model questions cover a range of topics and units within the Class 12 physics syllabus, and are designed to test students’ understanding of key concepts and principles.
By working through these model questions, students can get a sense of the types of questions they are likely to encounter on the actual exam, and can practice applying their knowledge to solve problems.
NEB Class 12 Physics Model Question 2079 is given as:
Download Class 12 Physics Model Question NEB 2079
In conclusion, the Class 12 physics syllabus, specific grid, curriculum, and model questions provided in this post are an essential resource for students preparing for the NEB board exam in 2079/2080.
By familiarizing themselves with the updated syllabus and curriculum, and by practicing with the model questions, students can ensure that they are well-prepared to succeed in their Class 12 physics exams. We hope that this post has been helpful in providing students with the tools and information they need to achieve their academic goals.





![NEB Class 12 Exam Routine 2081/2082 [2025]](https://iswori.com.np/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/neb-class-12-routine.png)

Hey!
Your website is so freaking good. I love the design and all the arrangement. Will you Please Tell me the name of the theme of this website. I really want to put it on my own website.Have a good day.