Class 11 Account Model Question With Solution
CDC Provided Updated NEB Class 11th Account Subject Model Question 2080 Solution PDF for Upcoming Board Exam 2081. This new Class 11 Model Question is based on Latest NEB Syllabus.
| Class 11 Account Model Question Solution 2080 | |
|---|---|
| Grade | Class 11 (XI) |
| Question Type | Model Question |
| Year | 2080-2081 |
| Total Marks | 75 Marks |
| Total Time | 3 Hours |
| Source | National Education Board |
| Provided by | Class 11 Model (All Subject) Iswori Education |
Section A: Very Short Answer Questions
Attempt All Questions [11 x 1 mark = 11 marks]
Q: 1. What is book keeping?
Bookkeeping is the combination of two words ‘book and keeping’.
Book is the collection of financial data or information; keeping is the process of recording these data.
Q: 2. Mention any two objectives of accounting.
The main objective of bookkeeping is to find out financial transactions.
After finding out financial transactions, they must be classified into personal, real and nominal accounts.
Q: 3. Write the meaning of the money measurement concept.
According to the money measurement concept, only monetary terms are recorded.
It ignores those transactions that cannot be expressed in-term-of money.
Q: 4. Define trial balance.
According to the Microsoft Corporation, “Trial balance is a statement to check the debits and credits.”
Q: 5. What is a cross cheque?
When two slanted or parallel lines are drawn on the left-hand side of the cheque, it is known to cross of the cheque.
Cross cheque is deposited into account then the amount of cheque will be credited into the account.
Q: 6. Write about the error of principle.
When an accountant does not know properly about capital and revenue, the principle of error occurs.
Example: Salary paid to staff is debited to his/her personal account.
Q: 7. What is the reserve?
In accounting, a reserve means an amount keep aside out of profit.
Reserve helps to make strong financial position of the business firm.
Q: 8. Write any one difference between capital expenditure and revenue expenditure.
Differences between Capital and Revenue Expenditures
Bases | Capital expenditures | Revenue expenditures |
Purpose | It is incurred to purchase fixed assets or improve their life. | It is incurred to manage day-to-day business activities. |
Q: 9. What is dhapot?
Dhapot was final statement under syaha sresta pranali.
It was similar to the final accounts of the modern accounting system.
Q: 10. Define bank cash book.
A bank cash book is a book of account maintained by operating level offices in the government office.
In this book, cash and banking transactions are recorded.
Q: 11. State the use of the budget sheet.
A budget sheet is used for controlling budget expenditures.
It provides information about annual appropriation, budget release and budget expenditure.
Section B: Short Answer Questions
Attempt All Questions [8 x 5 marks = 40 marks]
Q: 12 A. State accounting process in brief.
A complete sequence of accounting procedures is an accounting process.
It is also popularly known by accounting cycle.
It includes recording, classifying, summarizing and interpreting.
An accounting cycle begins with the recording of transactions
and ending with the preparation and interpretation of the final account.
Accounting process is of cyclic and sequential order.
It is given in the following:
> Documenting the financial transactions
> Classifying and recording the financial transactions into the journals
> Posting the transactions into the respective ledger accounts
> Balancing the ledger accounts
> Preparing a trial balance
> Preparing the financial statements like Trading account, Profit and loss account and Balance sheet
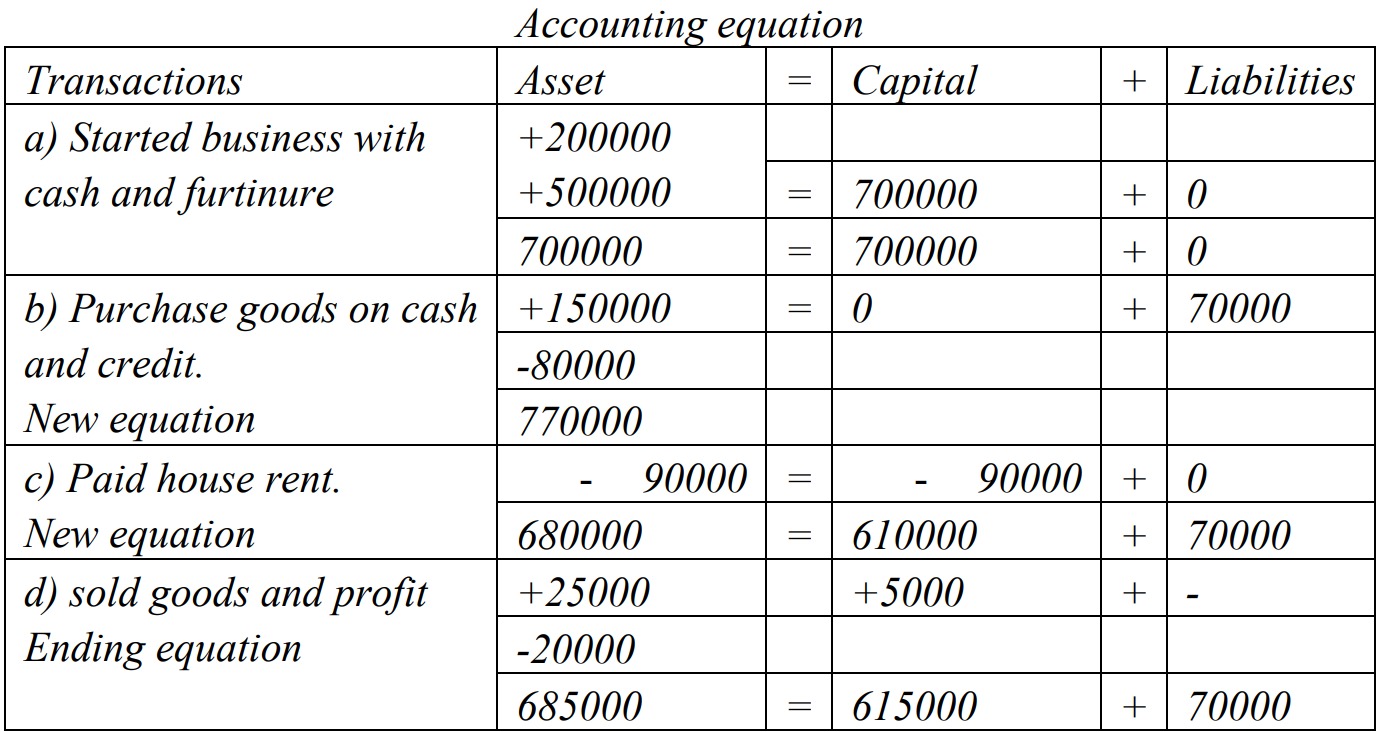
Q: 12 B. Prepare accounting equation from following details:
a. Started business with cash $ 200,000 and furniture $500,000
b. Purchase goods worth $80,000 on cash and 70,000 on credit.
c. Paid rent $90,000
d. Sold goods costing $20,000 in cash for $25,000.
[Answer: A = $685,000; C = $615,000; L = $70,000]
SOLUTION
Q: 13 A. Cash and banking transactions are given below by ABC Traders:
Sep 1: Opening balance of cash and bank are $60,000 and $200,000 respectively.
Sep 13: Cash deposited at the bank of $30,000.
Sep 22: Paid $32,000 to Ram through cheque for settling the account of $35,000.
Sep 27: Received a cheque from Aviral cheque of $19,000 and cash of $3,000 for selling the machine.
Required: Triple column cash book for the month
[Answer: Balance b/d: Cash = $33,000; Bank = $217,000]
(Assume Poush = September)
SOLUTION
Triple Column Cash Book

Q: 13 B. Transactions related to ABC Furniture House for the purchase of furniture are given below:
Dec 5: Purchase from Karuna Suppliers:
10 coffee tables for $100,000
20 small chairs @ $4,000 each
Trade discount @ 10%
Dec 19: Purchased from Anjali Traders:
5 beds @ 15,000 each
8 pieces of sofa @ $25,000 per sofa
Required: Purchase book
[Answer: Total creditors ($162,000 + $275,000) = $437,000]
SOLUTION
Purchase Book
In the book of ABC Furniture House

Q: 14. Following information are given by XYZ Traders:
(a) Cashbook showed a balance of $80,000.
(b) Bank credited $20,000 only out of various cheques of $75,000 deposited in the bank.
(c) Cheques were issued of $90,000 but a cheque of $10,000 was not presented for payment till the date.
(d) A customer deposited a cheque of $44,000 directly in the bank but has not been recorded in the cash book.
(e) Bank debited $500 as bank charge in the passbook.
(f) Cheque of $12,000 received and entered into the cash book but failed to deposit in the bank.
Required: Bank Reconciliation Statement [5]
[Answer: Balance as per passbook = $66,500]
SOLUTION
Bank Reconciliation Statement
For the month of ….
Particulars | Amount | Amount | |
Debit balance as per cashbook | 80,000 | ||
Add: | Cheque issued but not presented for payment | 10,000 | |
Customer directly deposited at the bank but not recorded in the cashbook | 44,000 | 54,000 | |
Less: | Cheque deposited into bank but not yet cleared (75,000 – 20,000) | 55,000 | |
Bank charge debited in the passbook | 500 | ||
Cheque entered into cashbook but failed to deposit at the bank | 12,000 | (67,500) | |
Balance as per passbook | 66,500 | ||
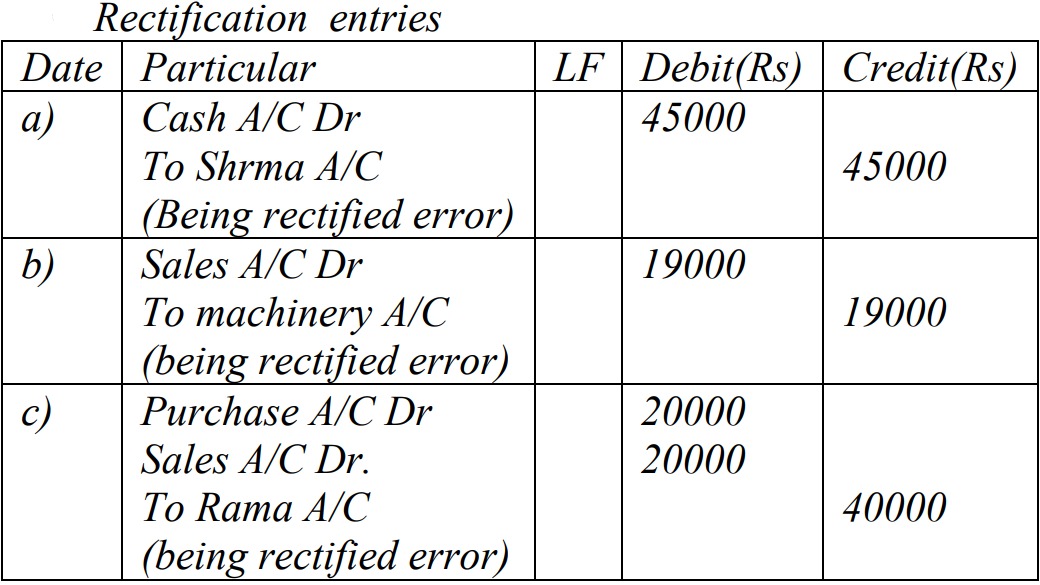
Q: 15 A. Rectify the following errors before preparing of trial balance. [3]
(a) Cash sales to Sharma $45,000 debited to his account
(b) Sales of machinery @ $19,000 were wrongly credited in the sales account.
(c) Purchase goods from Pema $20,000 recorded in the sales book.
[Answer: (a) Sharma credited $45,000;
(b) Machine credited $19,000;
(c) Pema credited $40,000]
SOLUTION
Rectified Journal Entry
Given and working note:

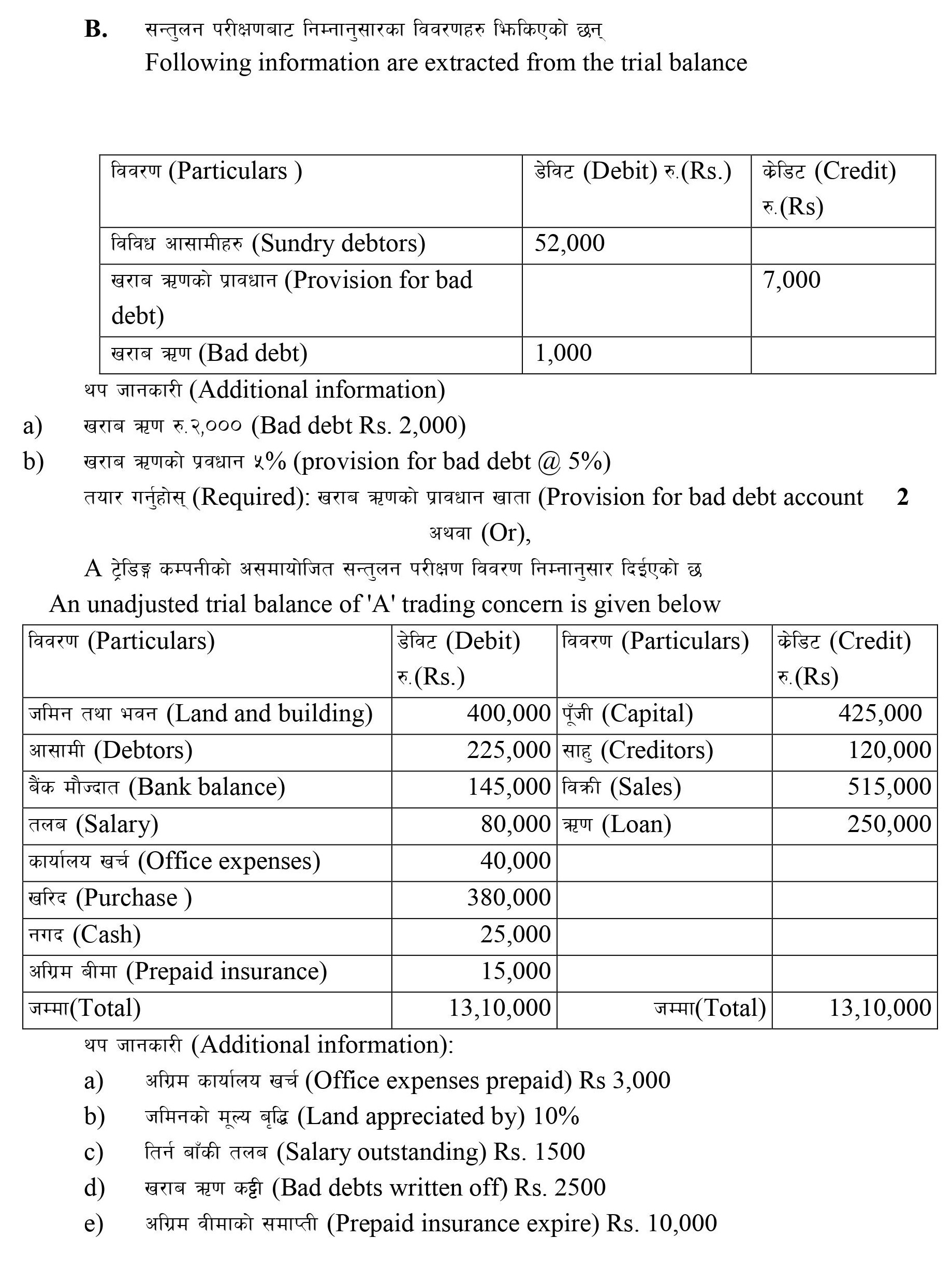
Q: 15 B. Following information are extracted from the trial balance:
Particulars | Amount Dr | Amount Cr |
Sundry debtors | 52,000 | |
Provision for bad debts | 7,000 | |
Bad debts | 1,000 |
Additional information:
a. Bad debt $2,000
b. provision for bad debt @ 5%
Required: Provision for bad debt account [2]
[Answer: To P&L (b/f) = $1,500]
SOLUTION
Provision for Bad Debt Account
Particulars | Amount | Particulars | Amount |
To Bad debts (old) | 1,000 | By Balance b/d | 7,000 |
To Bad debts (new) | 2,000 | ||
To P&L account (b/f) | 1,500 | ||
To Balance c/d | 2,500 | ||
($52,000 – $2,000) x 5% | |||
7,000 | 7,000 |
Or
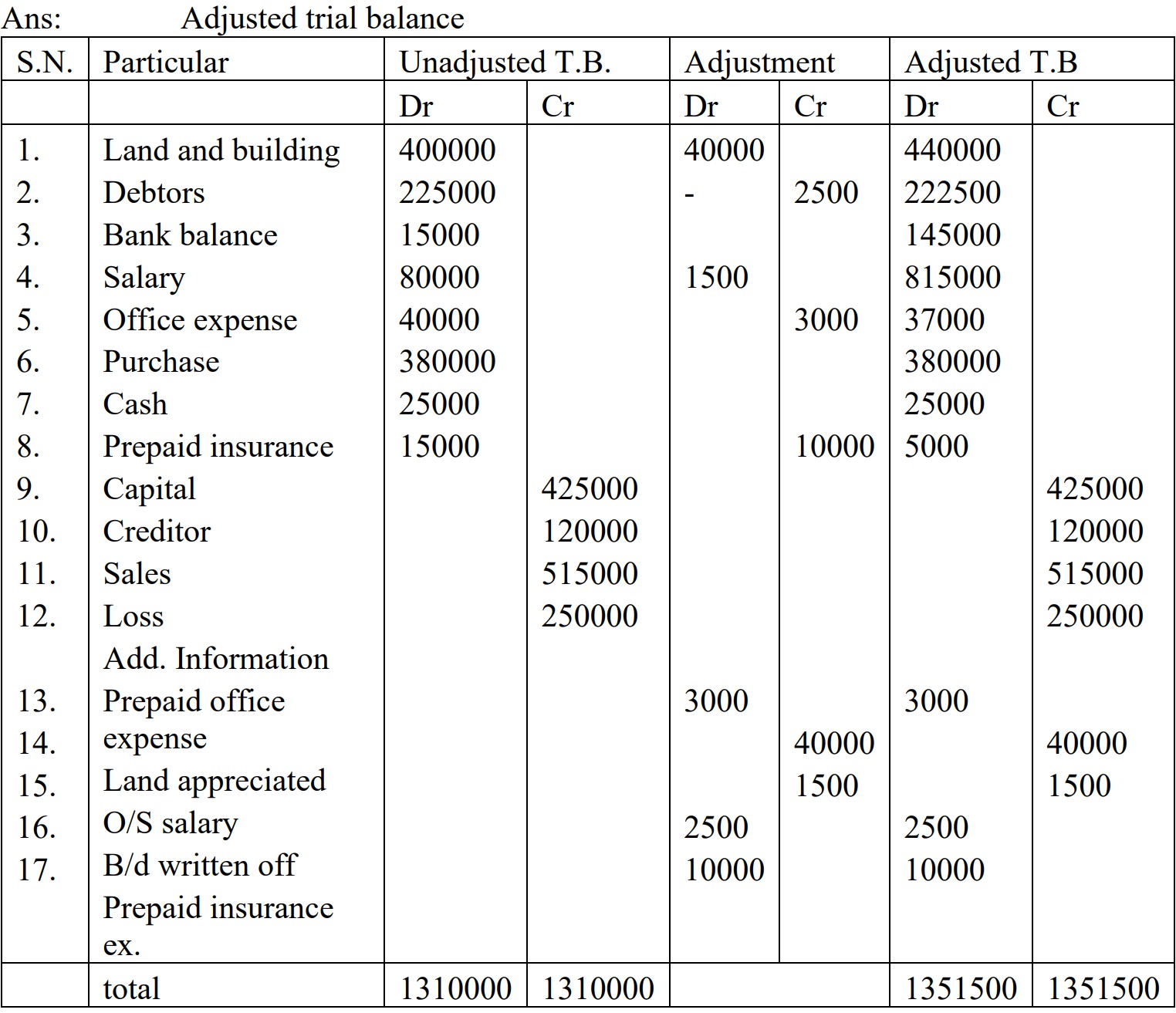
An unadjusted trial balance of ABC Trading Concern is given below:
Particulars | Amount Dr | Particulars | Amount Cr |
Land and building | 4,00,000 | Capital | 4,25,000 |
Debtors | 2,25,000 | Creditors | 1,20,000 |
Bank balance | 1,45,000 | Sales | 5,15,000 |
Salary | 80,000 | Loan | 2,50,000 |
Office expenses | 40,000 | ||
Purchase | 3,80,000 | ||
Cash | 25,000 | ||
Prepaid insurance | 15,000 | ||
13,10,000 | 13,10,000 |
Additional information:
Office expenses prepaid $3,000
Land appreciated by 10%
Salary outstanding $1,500
Bad debts written off $2,500
Prepaid insurance expire $10,000
Required: Adjusted Trial balance [5]
[Answer: Adjustment = $57,000; Adjusted TB = $13,51,000]
SOLUTION
Journal Entry
Date | Particulars | LF | Amount Dr | Amount Cr | |
Prepaid office expenses | Dr | 3,000 | |||
To Office expenses | 3,000 | ||||
(Being: office expenses paid in advance) | |||||
Land and building | Dr | 40,000 | |||
To Appreciation on land | 40,000 | ||||
(Being: appreciation on land viz 400,000 x 10%) | |||||
Salary account | Dr | 1,500 | |||
To Salary payable | 1,500 | ||||
(Being: salary payable) | |||||
Bad debts account | Dr | 2,500 | |||
To debtors account | 2,500 | ||||
(Being: bad debts written off) | |||||
Prepaid insurance expired account | Dr | 10,000 | |||
To Prepaid insurance | 10,000 | ||||
(Being: prepaid insurance expired) | |||||
Adjusted Trial Balance
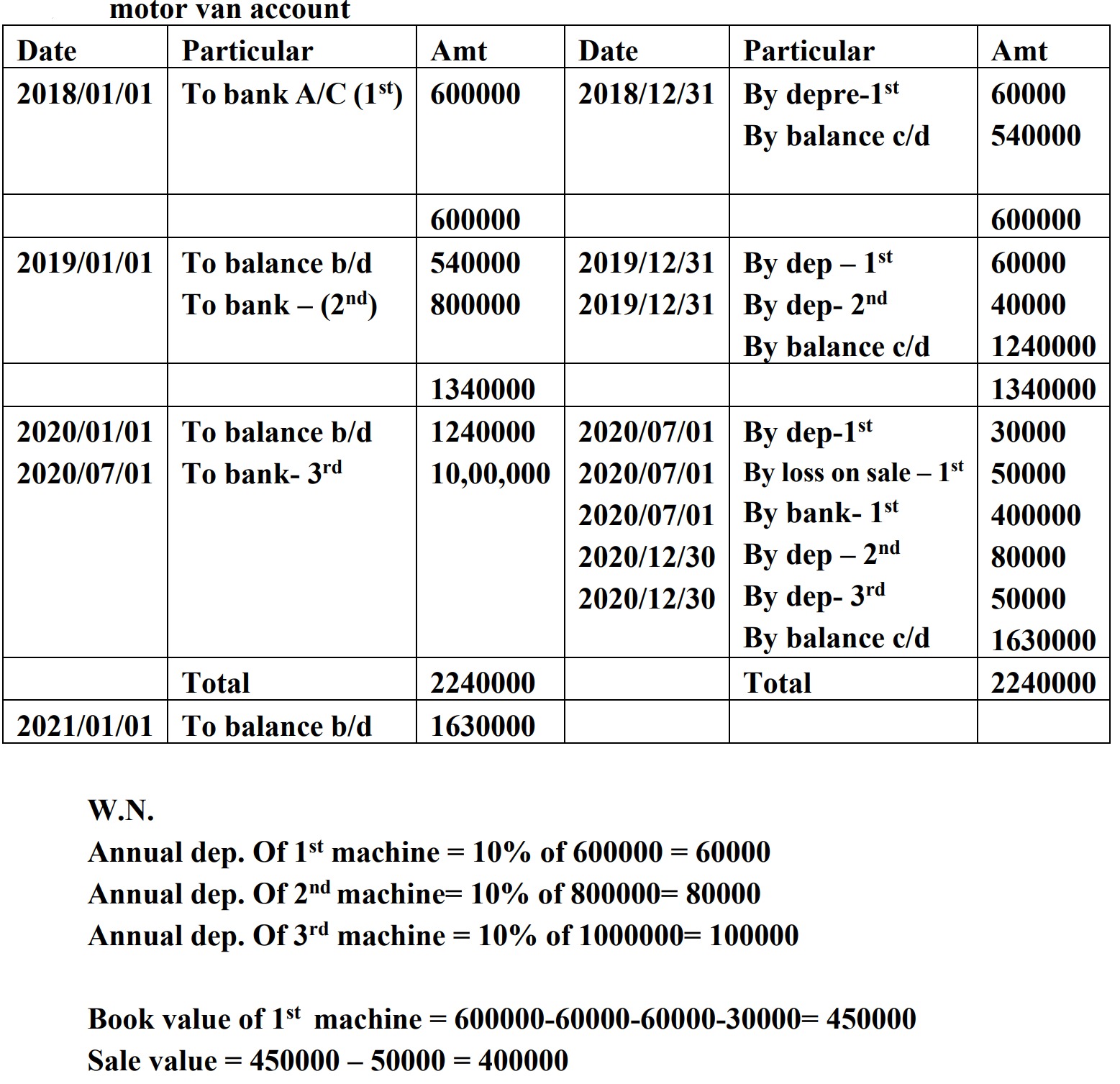
Q: 16. On 1st January 2018 ABC Company purchased a motor van for $6,00,000. On 1st July 2019, the company purchased another van worth $8,00,000. On 1st
July 2020, the first motor van was sold bearing the loss of $50,000 and
on the same date, the company purchased another van for $10,00,000.
Depreciation was charged @10% p.a. under the fixed installment method.
The accounts of the company were closed on 31st December each year.
Required: Motor van account for the first three years [1+2+2 = 5]
[Answer: Depreciation in 2018 = $60,000;
Depn in 2019 ($60,000 + $40,000) = $100,000;
Depn in 2020 ($30,000 sold + $80,000 + $50,000);
Balance on 31 Dec 2020 = $16,30,000;
Loss (given); CSV (450,000 – 50,000 loss) = $400,000
SOLUTION
Given and working note:
Depreciation @ 10% p.a. on FIM
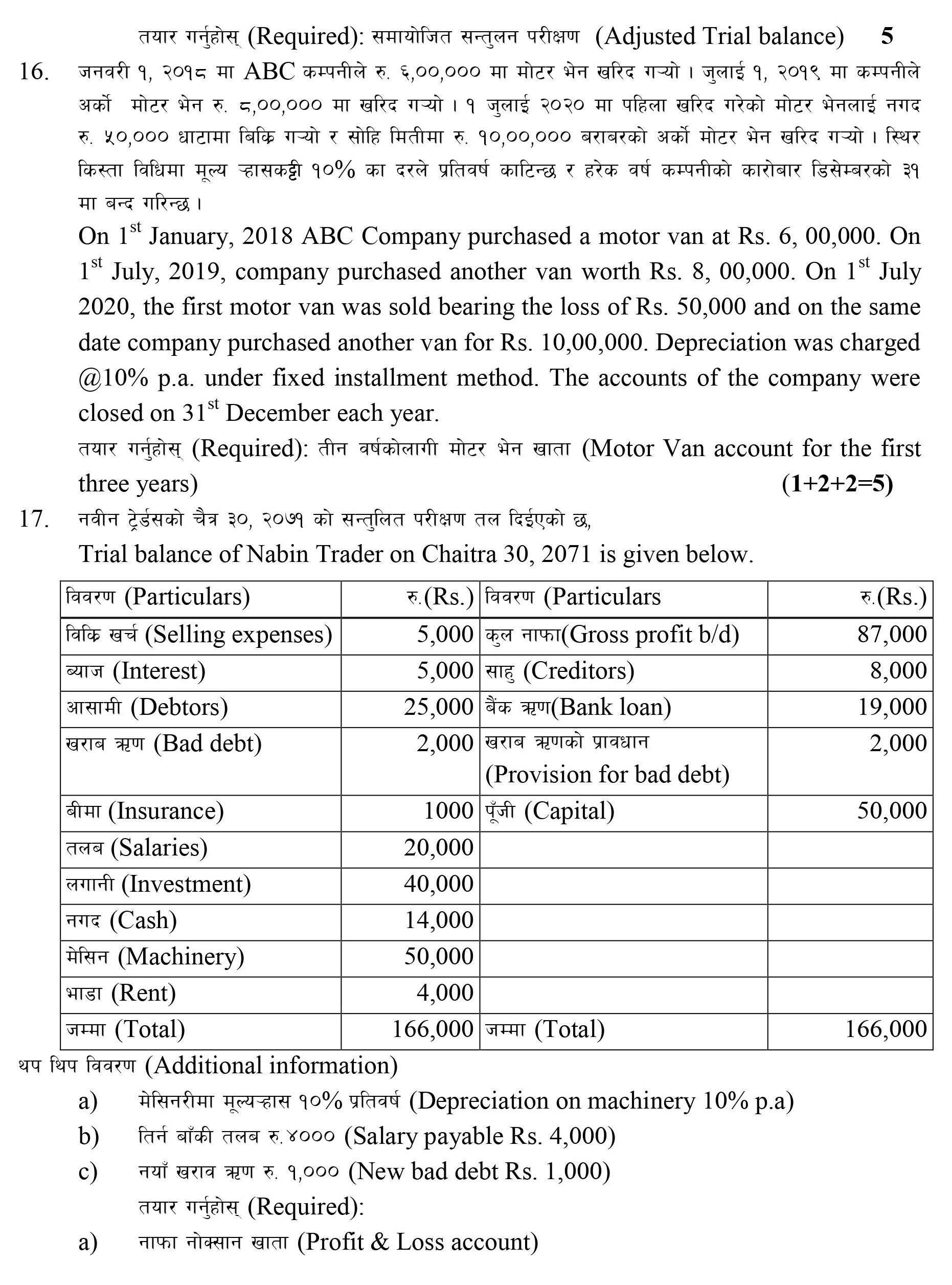
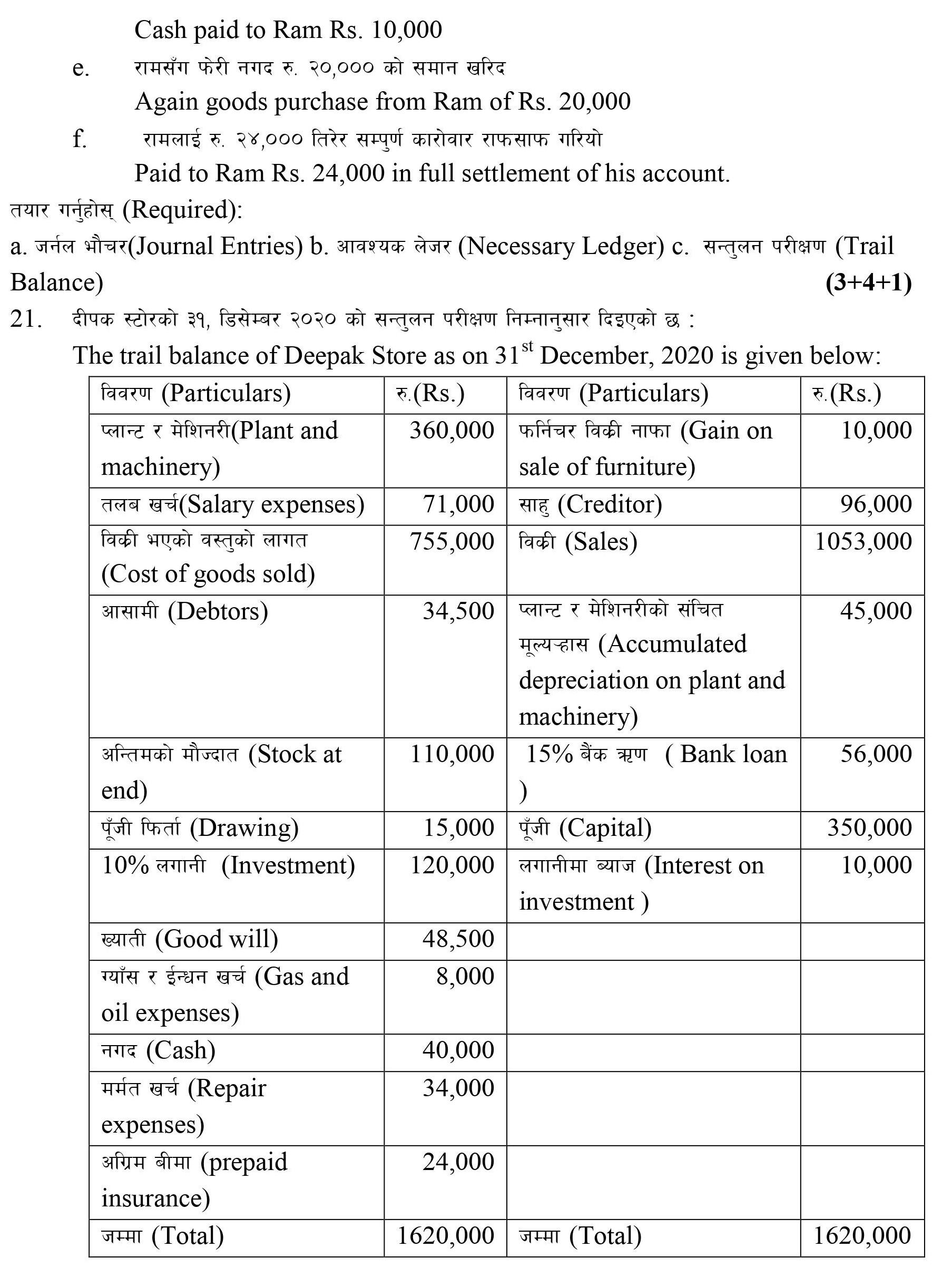
Q: 17. Trial balance of Nabin Trader on 31st December 2021 is given below:
Particulars | Amount Dr | Particulars | Amount Cr |
Selling expenses | 5,000 | Gross profit b/d | 87,000 |
Interest | 5,000 | Creditors | 8,000 |
Debtors | 25,000 | Bank loan | 19,000 |
Bad debts | 2,000 | Provision for bad debts | 2,000 |
Insurance | 1,000 | Capital | 50,000 |
Salaries | 20,000 | ||
Investment | 40,000 | ||
Cash | 14,000 | ||
Machinery | 50,000 | ||
Rent | 4,000 | ||
166,000 | 166,000 |
Additional information:
a. Depreciation on machinery 10% p.a.
b. Salary payable $4,000
c. New bad debt $1,000
Required: (i) Profit and loss account; (ii) Balance sheet [3+2]
[Answer: Net profit = $42,000; BS = $123,000]
SOLUTION

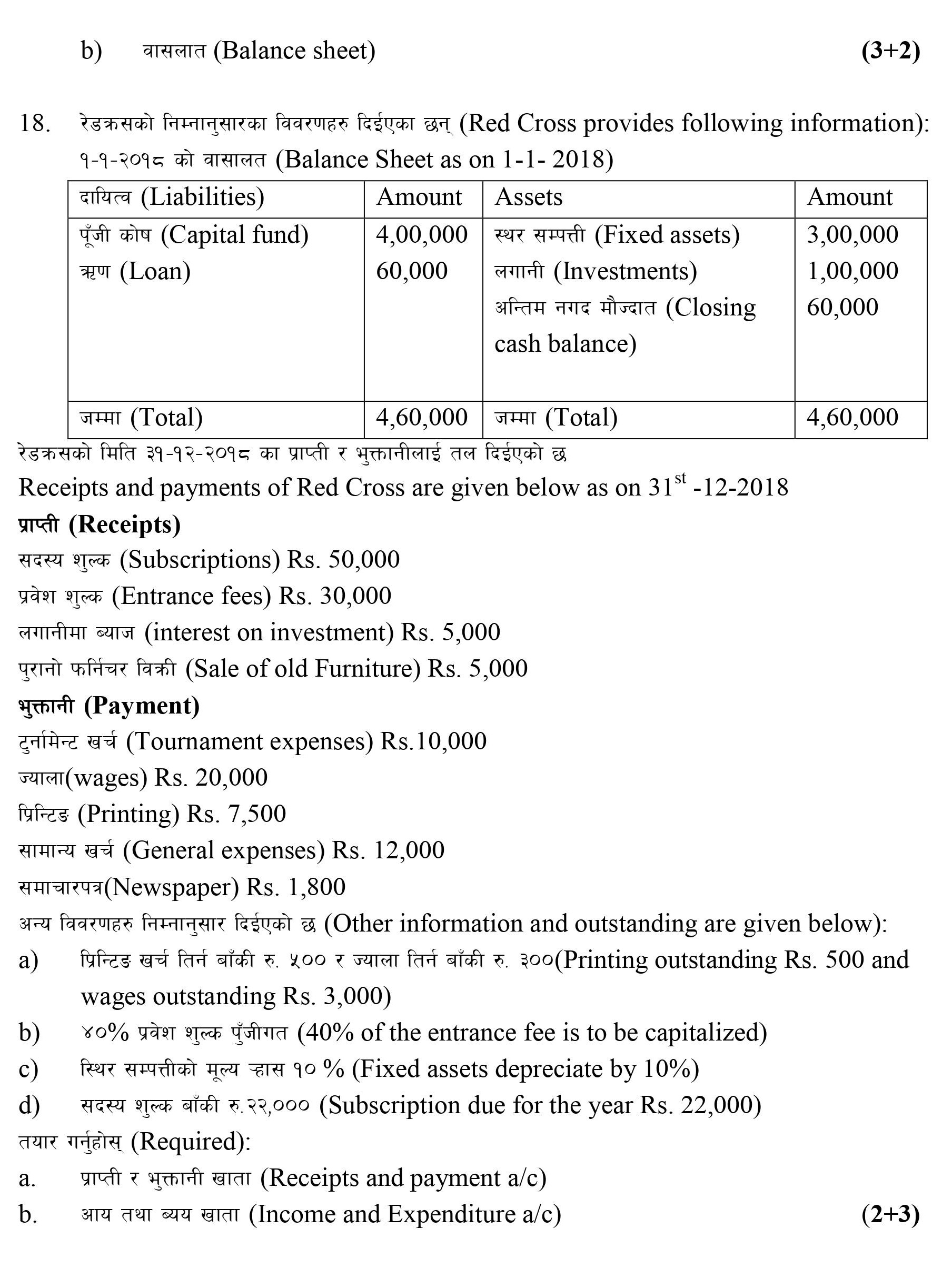
Q: 18. RC Club provides the following information:
Balance Sheet as on 1-1- 2020
Liabilities | Amount Dr | Assets | Amount Cr |
Capital fund | 400,000 | Fixed assets | 300,000 |
Loan | 60,000 | Investment | 100,000 |
Closing cash balance | 60,000 | ||
460,000 | 460,000 |
Receipts and payments of Red Cross are given below as on 31st
-12-2018
(Receipts)
(Subscriptions) Rs. 50,000
(Entrance fees) Rs. 30,000
(interest on investment) Rs. 5,000 L
(Sale of old
Furniture) Rs. 5,000 L (Payment)
(Tournament expenses) Rs.10,000
(wages) Rs. 20,000
(Printing) Rs. 7,500
(General expenses) Rs. 12,000
(Newspaper) Rs. 1,800
(Other information and outstanding are given below):
a) (Printing outstanding Rs. 500 and wages outstanding Rs. 3,000)
b) (40% of the entrance fee is to be capitalized)
c) (Fixed assets depreciate by 10%)
d) (Subscription due for the year Rs. 22,000)
(Required):
a. (Receipts and payment a/c)
b. (Income and Expenditure a/c)
SOLUTION

Q: 19 A. Shweta keeps her account under the single entry system. She started a business with $200,000 on 1st
Jan 2020. She withdraws $2,000 per month for household work. The
position of her business at the end of the year was as follows:
Fixed assets | 190,000 | Creditors | 50,000 |
Inventory | 85,000 | Debtors | 40,000 |
Due expenses | 10,000 | Bank balance | 60,000 |
Required: (i) Closing statement of affairs; (ii) Statement of profit and loss [1+1 = 2]
[Answer: Closing capital = $315,000; Profit = $139,000]
SOLUTION
Statement of Affairs
As on 31 December 2020
Liabilities | Amount | Assets | Amount |
Due expenses | 10,000 | Fixed assets | 190,000 |
Creditors | 50,000 | Inventory | 85,000 |
Closing capital (b/f) | 315,000 | Debtors | 40,000 |
Bank balance | 60,000 | ||
375,000 | 375,000 |
Profit and Loss Statement
Particulars | Amount | Amount |
Closing capital | 315,000 | |
Add: Drawings ($2,000 x 12) | 24,000 | |
339,000 | ||
Less: Opening capital | (200,000) | |
Net profit for the year | 139,000 |
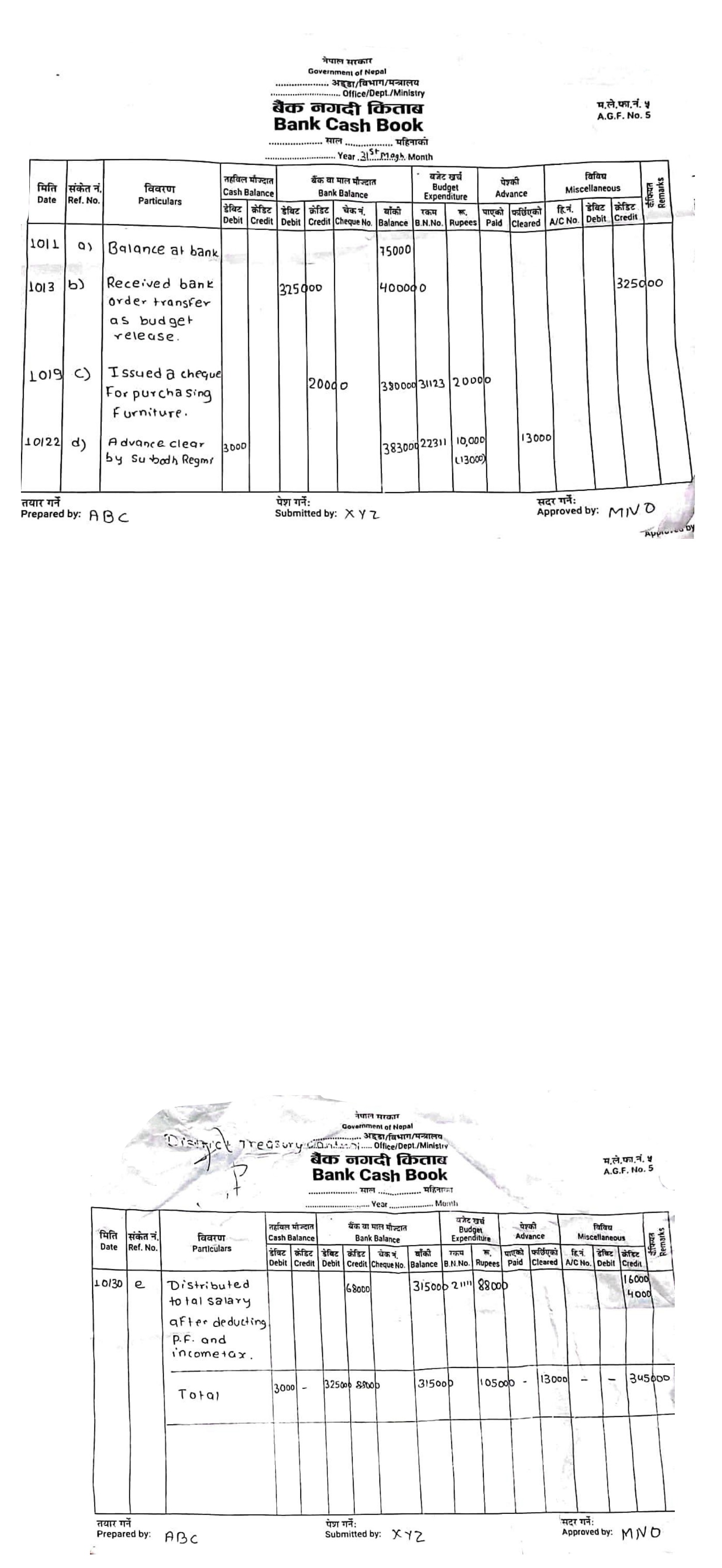
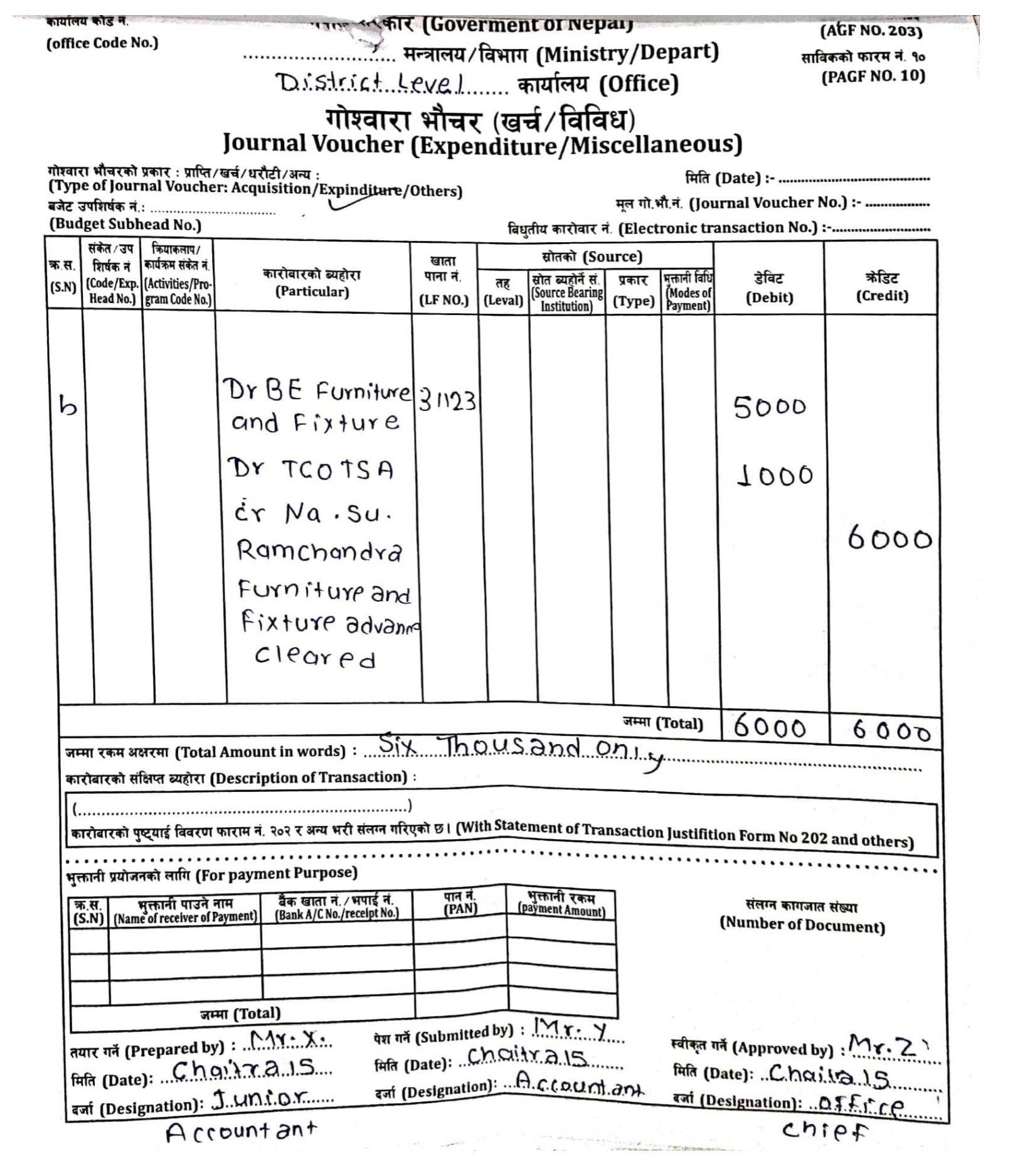
Q: 19 B. Following transactions of District Level Office are given:
(a) | Dec 1 | House rent @ $8,000 per month for three months paid to house owner Sailesh. |
(b) | Dec 15 | Furniture advance of $5,000 was cleared as per bill of $6,000 and bank voucher of $1,000 submitted by Na. Su. Ramchandra |
(c) | Dec 30 | Staff remuneration of Kartik $30,000 (without provident fund) was distributed after deducting PF $6,000, social security $300 and income tax $1,500. |
Required: Journal vouchers
[Answer: (a) Advance rent = $24,000;
(c) Total salary = $33,000; DTCO = $25,200]
*Month has been changed, December = Chaitra
SOLUTION

Or
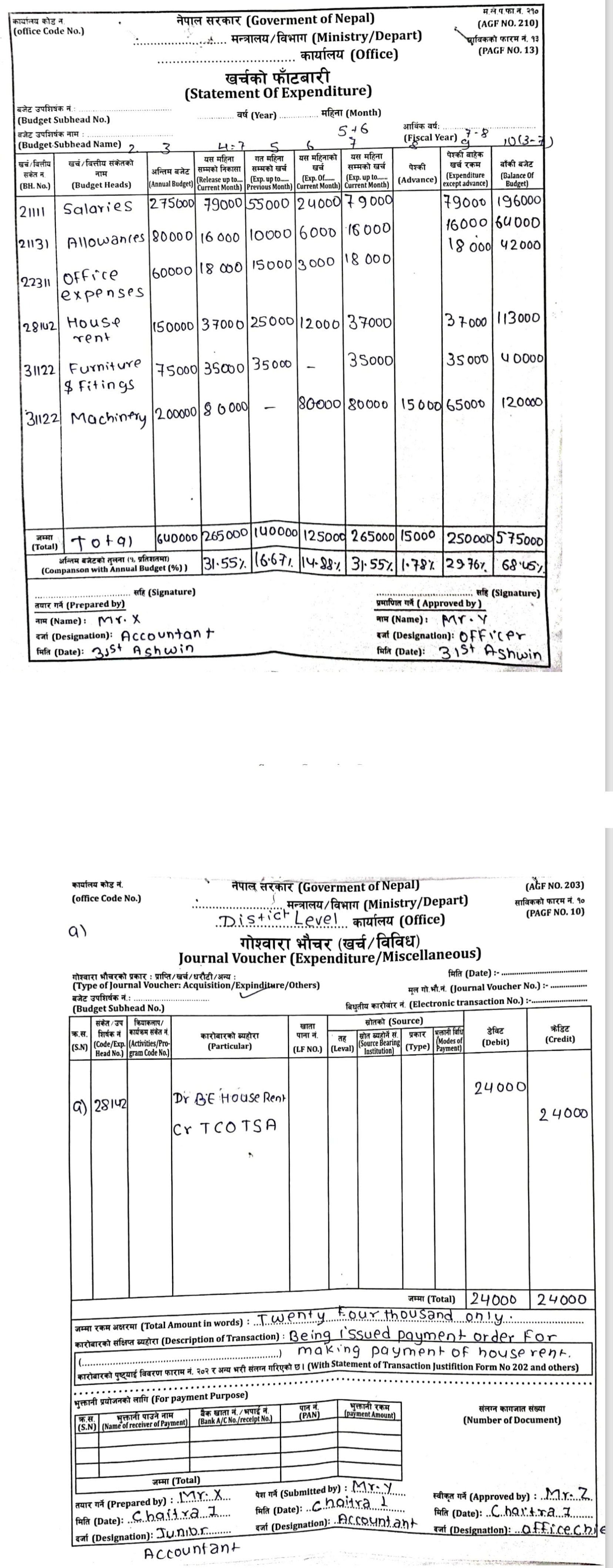
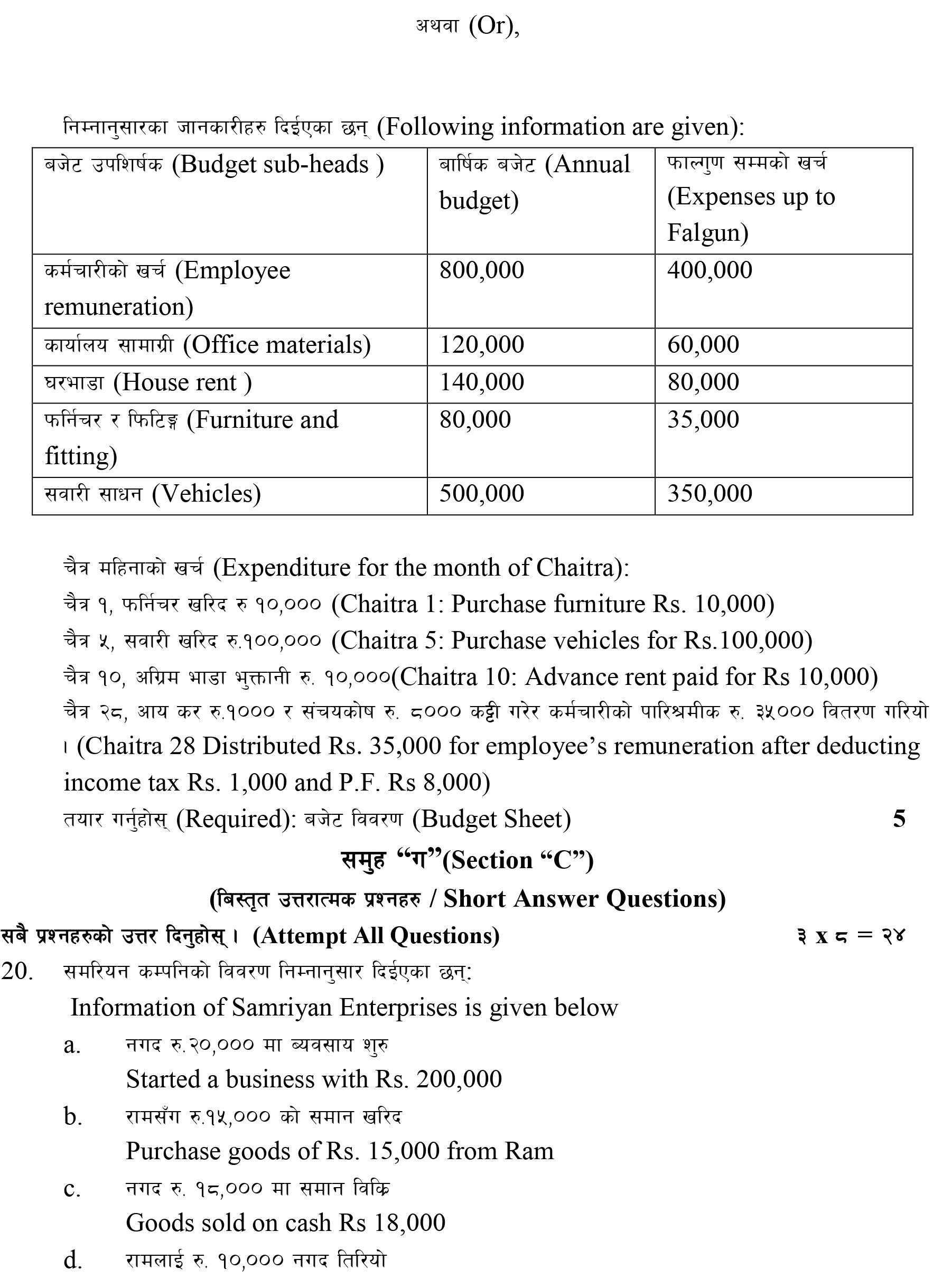
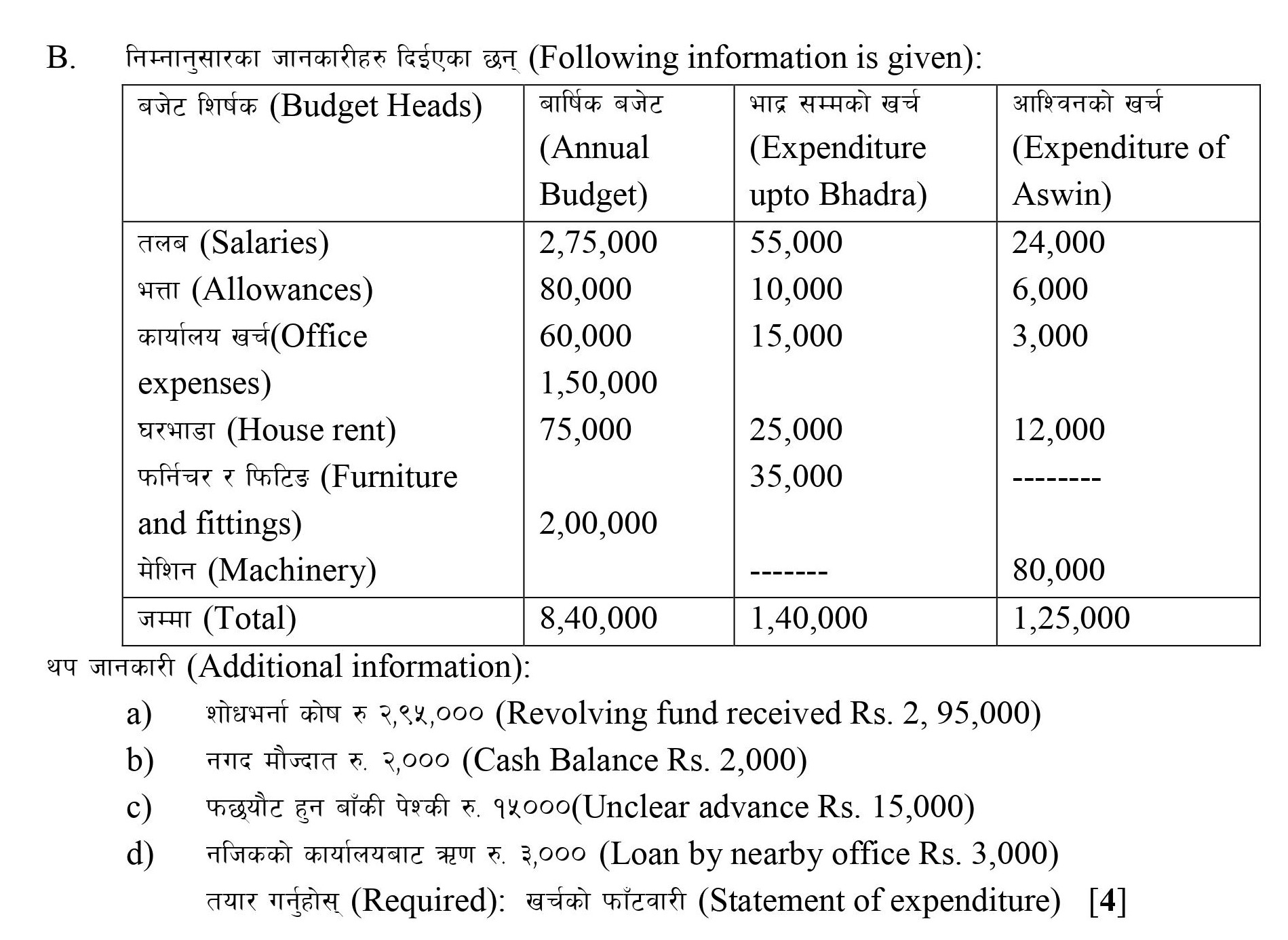
Following information are given by the Local Level Office:
Budget sub-head | Annual budget | Expenses upto November (Falgun) |
Employee remuneration | 800,000 | 400,000 |
Office materials | 120,000 | 60,000 |
House rent | 140,000 | 80,000 |
Furniture and fitting | 80,000 | 35,000 |
Vehicles | 500,000 | 350,000 |
Expenditure for the month of December (Chaitra):
Dec 1: Purchase furniture $10,000
Dec 5: Purchase vehicles for $100,000
Dec 10: Advance rent paid for $10,000
Dec 28 Distributed $35,000 for employee’s remuneration after deducting income tax $1,000 and PF $8,000.
Required: Budget sheet [5]
[Answer: Balance of budget: $551,000]
SOLUTION

Given and working note:
Dr BE Salary (b/f) 44,000
Cr IT 1,000
Cr PF 8,000
Cr DTCO 35,000
Section C: Long Answer Questions




Or
What is government accounting? Explain the features of the new government accounting system. [3+5 = 8]
Government accounting
Every state or country has its own government.
It records the financial transactions of the government offices.
The government accounting system is used in government offices to record and report their financial transactions.
Systematic and scientific recording of government revenues and expenditures are recorded in it.
In this account, revenues collecting, recording, classifying, summarizing, interpreting and expenditures are recorded.
It reveals how public funds have been generated and utilized for the welfare of the general public.
Features of new government accounting system
The main features of the new accounting system are explained below:
Based on the double-entry system
The new accounting system is based on the principle of a double entry system of bookkeeping.
In a double entry system, each financial transaction has two aspects i.e. debit and credit.
Each financial transaction affects one debit side and another credit side.
Uniformity and simplicity
New accounting systems are used in the entire government offices in Nepal.
This system is simple to understand and easy to operate; because it is based on the principle of a double entry system.
Banking transaction
Cash is the probability of misuse and manipulation of object.
New accounting systems emphasize banking transactions.
Every government officer should deposit all revenues into the bank and payments are made through DTCO.
Classification of offices
Government organizations are classified into central level offices and local level offices.
Central level offices are ministry.
Operating level offices are operated in a metropolitan city, a sub-metropolitan city, municipality and rural municipality.
Based on budget heads
The new accounting systems are based on different budget heads for making expenditures.
Government officers should not make expenditures more than allocated to a budget head.

Class 11th Compulsory Account Model Question (Images)





Class 11th Compulsory Account PDF Download


